|
July 27, 2013
A colleague and friend ______ ______ turned me on to the previous article and then to this one and I wanted to share both because I believe you (Dr. Holly) have "Kaizen" and you are not a for-profit, multinational corporation, but a doctor working in a border town in Texas who's sharing of Kaizen has far reaching systemic impact! Best Richard Cohen YAI NYC (emphasis added)
Definition of Kaizen
Kaizen is a system of continuous improvement in quality, technology, processes, company culture, productivity, safety and leadership.
Kaizen was created in Japan following World War II. The word Kaizen means "continuous improvement". It comes from the Japanese words 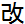 ("kai") which means "change" or "to correct" and ("kai") which means "change" or "to correct" and 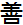 ("zen") which means "good". Kaizen is a system that involves every employee - from upper management to the cleaning crew. Everyone is encouraged to come up with small improvement suggestions on a regular basis. This is not a once a month or once a year activity. It is continuous. Japanese companies, such as Toyota and Canon, a total of 60 to 70 suggestions per employee per year are written down, shared and implemented. ("zen") which means "good". Kaizen is a system that involves every employee - from upper management to the cleaning crew. Everyone is encouraged to come up with small improvement suggestions on a regular basis. This is not a once a month or once a year activity. It is continuous. Japanese companies, such as Toyota and Canon, a total of 60 to 70 suggestions per employee per year are written down, shared and implemented.
In most cases these are not ideas for major changes. Kaizen is based on making little changes on a regular basis: always improving productivity, safety and effectiveness while reducing waste. Suggestions are not limited to a specific area such as production or marketing. Kaizen is based on making changes anywhere that improvements can be made. Western philosophy may be summarized as, "if it ain't broke, don't fix it." The Kaizen philosophy is to "do it better, make it better, improve it even if it isn't broken, because if we don't, we can't compete with those who do."
Kaizen in Japan is a system of improvement that includes both home and business life. Kaizen even includes social activities. It is a concept that is applied in every aspect of a person's life. In business Kaizen encompasses many of the components of Japanese businesses that have been seen as a part of their success. Quality circles, automation, suggestion systems, just-in-time delivery, Kanban and 5S are all included within the Kaizen system of running a business.
Kaizen involves setting standards and then continually improving those standards. To support the higher standards Kaizen also involves providing the training, materials and supervision that is needed for employees to achieve the higher standards and maintain their ability to meet those standards on an on-going basis.
July 26, 2013
In Lieu of Money, Toyota Donates Efficiency to New York Charity
By MONA EL-NAGGAR
The Food Bank for New York City is the country’s largest anti-hunger charity, feeding about 1.5 million people every year. It leans heavily, as other charities do, on the generosity of businesses, including Target, Bank of America, Delta Air Lines and the New York Yankees. Toyota was also a donor. But then Toyota had a different idea.
Instead of a check, it offered kaizen.
A Japanese word meaning “continuous improvement,” kaizen is a main ingredient in Toyota’s business model and a key to its success, the company says. It is an effort to optimize flow and quality by constantly searching for ways to streamline and enhance performance. Put more simply, it is about thinking outside the box and making small changes to generate big results.
Toyota’s emphasis on efficiency proved transformative for the Food Bank.
At a soup kitchen in Harlem, Toyota’s engineers cut down the wait time for dinner to 18 minutes from as long as 90. At a food pantry on Staten Island, they reduced the time people spent filling their bags to 6 minutes from 11. And at a warehouse in Bushwick, Brooklyn, where volunteers were packing boxes of supplies for victims of Hurricane Sandy, a dose of kaizen cut the time it took to pack one box to 11 seconds from 3 minutes.
Toyota has “revolutionized the way we serve our community,” said Margarette Purvis, the chief executive and president of the Food Bank.
But Toyota’s initial offer to the charity in 2011 was met with apprehension.
“They make cars; I run a kitchen,” said Daryl Foriest, director of distribution at the Food Bank’s pantry and soup kitchen in Harlem. “This won’t work.”
When Toyota insisted it would, Mr. Foriest presented the company with a challenge.
“The line of people waiting to eat is too long,” Mr. Foriest said. “Make the line shorter.”
Toyota’s engineers went to work. The kitchen, which can seat 50 people, typically opened for dinner at 4 p.m., and when all the chairs were filled, a line would form outside. Mr. Foriest would wait for enough space to open up to allow 10 people in. The average wait time could be up to an hour and a half.
Toyota made three changes. They eliminated the 10-at-a-time system, allowing diners to flow in one by one as soon as a chair was free. Next, a waiting area was set up inside where people lined up closer to where they would pick up food trays. Finally, an employee was assigned the sole duty of spotting empty seats so they could be filled quickly. The average wait time dropped to 18 minutes and more people were fed.
The unusual partnership between Toyota and the Food Bank, which one Food Bank coordinator compared to a cultural exchange program, highlights a different way for-profit businesses can help their communities, experts said.
“It’s a form of corporate philanthropy but instead of giving money, they’re sharing expertise,” said David J. Vogel, a professor and an expert in corporate social responsibility at the Haas School of Business at the University of California, Berkeley. “It’s quite new.”
And many nonprofit organizations, facing tighter budgets as financing from federal and local governments diminishes, are having to make smarter business decisions.
“Nonprofit organizations are taking on what happens in the for-profit world because they will run better,” said Ronald P. Hill, a professor of marketing and business law at Villanova University.
In the early 1990s, Toyota limited sharing its expertise to its auto parts suppliers. But as the Toyota Production System Support Center, the company’s headquarters of efficiency, came to recognize broader interest in the Toyota model, the company offered consulting-style services to nonautomotive manufacturers and nonprofit organizations. Today, the center supports about 40 organizations, half of which are small to midsize manufacturers that pay a small fee. The rest are nonprofits, like the Food Bank, that get the services free.
“There’s a lot of opportunities in a variety of industries to improve and become more competitive by applying the Toyota production system,” said Jaime Bonini, the support center’s general manager.
The lessons provided by Toyota come at a critical time for the Food Bank as it faces increasing demand in a weak economy.
“From banks to restaurants to airlines, people give money and time and we’re grateful,” Ms. Purvis said. “But, it’s very rare for people to come and say, ‘You know what, this is the model that made our company great and we will share it with a charity with the hope that it will provide for the neediest people in your city.' ”
At the Project Hospitality food pantry on Staten Island, which is part of the Food Bank network, Toyota engineers tried to expedite the pickup process. They drew a layout identifying spots where there were slowdowns. They reorganized the shelves by food groups and used colored tape to mark the grain, vegetable, fruit and protein sections. The time clients spent in the pantry was reduced nearly by half.
Similarly, the Food Bank called on Toyota engineers to help one of its affiliated charities, Metro World Child, keep up with demand in the Far Rockaways after Hurricane Sandy.
Lisa Richardson, an engineer with a background in manufacturing, watched as volunteers walked around a warehouse in Brooklyn and scrambled to pack boxes of food. So she created an assembly line and volunteers dropped food items into boxes as they moved across a conveyor belt. The average time to pack one box shrank to 11 seconds from 3 minutes.
Still not satisfied, Ms. Richardson changed the size of the boxes.
“There was a lot of empty space in the box and they were shipping that air out in the truck,” Ms. Richardson said. The Food Bank was using standard boxes of 12 square inches.
By changing the size to 16 by 8 by 8, workers can pack each box more tightly and more boxes can go out in each truck.
Next up, Ms. Purvis says, is a plan “to kaizen” the Food Bank’s 90,000-square-foot warehouse in the Bronx, where Toyota will try to optimize use of the space and figure out delivery routes, among other tasks.
“I never thought that what we needed were a bunch of engineers,” Ms. Purvis said. “In our world food is king, but we didn’t know that the queen would be kaizen.”
James (Larry) Holly, M.D.
C.E.O. SETMA
www.jameslhollymd.com
Adjunct Professor
Family & Community Medicine
University of Texas Health Science Center
San Antonio School of Medicine
Clinical Associate Professor
Department of Internal Medicine
School of Medicine
Texas A&M Health Science Center
|