|
Dyslipidemia is one of six major, independent cardiovascular disease risk factors, The aggressive and successful management of lipids is critical to the well being of anyone with diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, or high risk for heart disease. SETMA's Lipids Suite of Templates provides a foundation for the treatment of .
The Lipids Suite of Templates can be accessed from:
AAA Home
NextGen's Main Tool Bar's Template Icon
- When the Template button is clicked you will be presented with the preference list.
- If the Diabetes Master Template is listed as one of your preferences, select it.
- If it is not one of your preferences, select the All radio button and then scroll down
until you find it in the list.
NOTE: For more on how to set up your preferences, Click Here
- All other disease management suites of templates
The organization and content of SETMA's Lipids Suite of Templates is as follows.
Master Lipids Template
The Maser Lipids Template is organized into four columns:
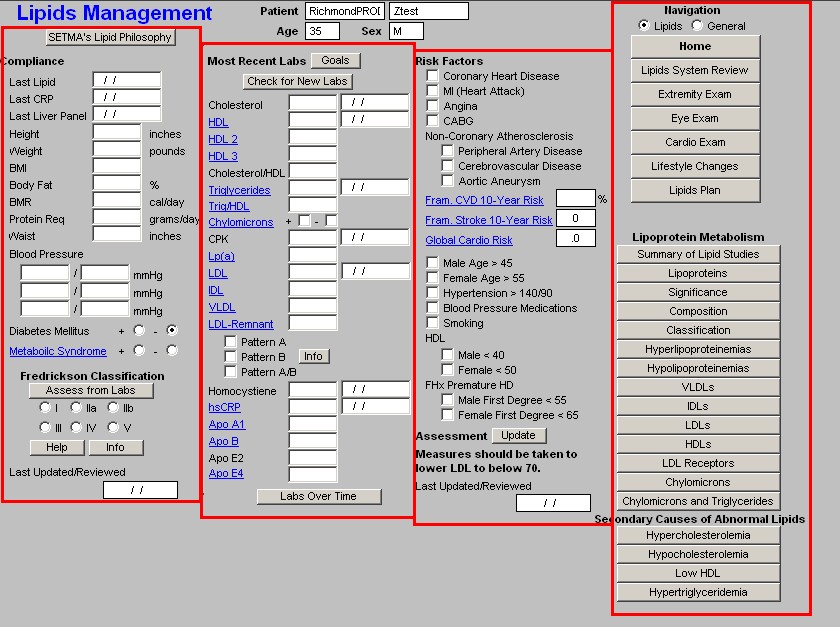
Column 1 --
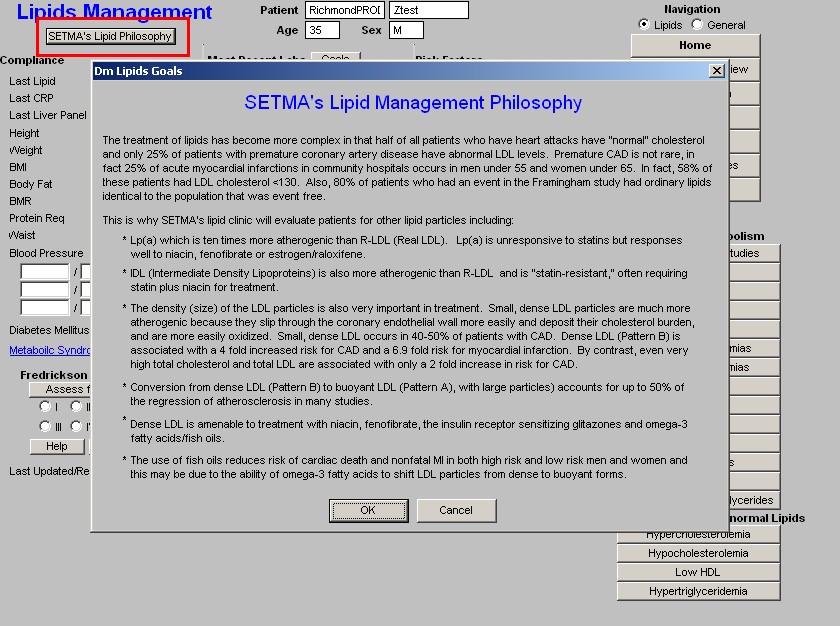
At the top, is a button entitled "SETMA's Lipid Philosophy"; the pop-up which is launched by depressing this button states:
"The treatment of lipids has become more complex in that half of all patients who have heart attacks have 'normal' cholesterol and only 25% of patients with premature coronary artery disease have abnormal LDL levels. Premature CAD is not rare in fact 25% of acute myocardial infarctions in community hospitals occur in men under 55 and women under 65. In fact, 58% of these patients had LDL cholesterol less than 130. Also, 80% of patients who had an event in the Framingham study had ordinary lipid identical to the population that was event free.
This is why SETMA's lipid clinic will evaluate patients for other lipid particles including:
- Lp(a) which is ten times more atherogenic than R-LDL (Real LDL). Lp(a) is unresponsive to statins but responses well to niacin, fenofibrate or estrogen/raloxifene.
- IDL (Intermediate Density Lipoproteins) is also more atherogenic than R-LDL and is "statin- resistant," often requiring statin plus niacin for treatment
- The density (size) of the LDL particles is also very important in treatment. Small, dense LDL particles are much more atherogenic because they slip through the coronary endothelial wall more easily and deposit their cholesterol burden, and are more easily oxidized. Small, dense LDL occurs in 40-50% of patients with CAD. Dense LDL (Pattern B) is associated with a 4 fold increased risk for CAD and a 6.9 fold risk for myocardial infarction, by contrast, even very high total cholesterol and total LDL are associated with only a 2-fold increase in risk for CAD.
- Conversion from dense LDL (Patter B) to buoyant LDL (Pattern A), with larger particles, accounts for up to 50% of the regression of atherosclerosis in many studies.
- Dense LDL is amenable to treatment with niacin, fenofibrate, the insulin receptor sensitizing glitazones and omega-3 fatty acids (fish oils).
- The use of fish oils reduces risk of cardiac death and nonfatal MI in both high risk and low risk men and woman and this my b due to the ability of omega-3 fatty acids to shift LDL particles from dense to forms."
Note: In order to evaluate many of these lipid particles specialized lipids testing such as the VAP test must be ordered. However, most insurance companies do not cover these tests; therefore, the patient will need to know their responsibility for payment for these tests before they are performed. Beneath this button are the following:
Compliance
- Last Lipid - this displays the date of the last lipid lab values. This is automatically updated from the lab order templates.
- Last CRP - c - reactive protein - this displays the date of the last hsCRP. This is automatically updated from the lab order templates.
- Last Liver Panel - this displays the date of the last live panel. This is automatically updated from the lab order templates.
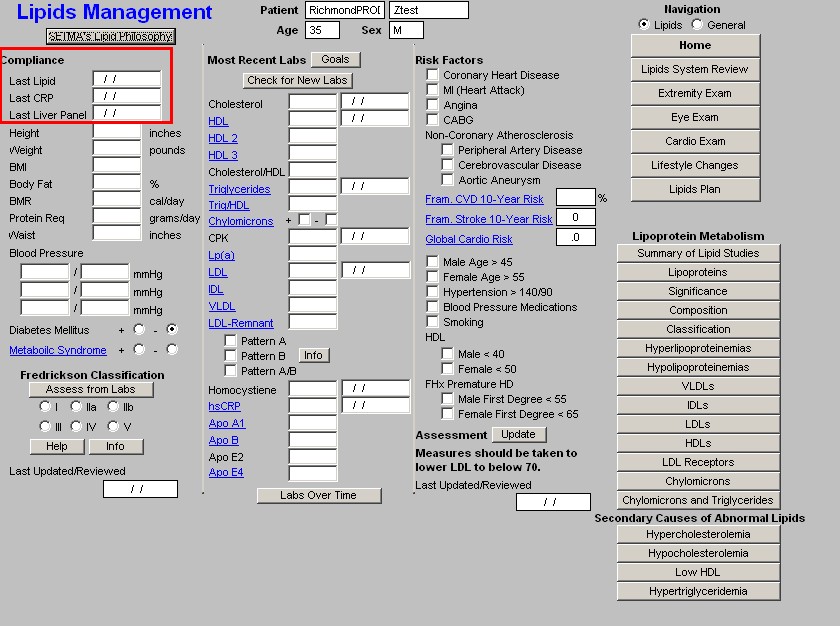
Vital Signs
- Height
- Weight
- BMI
- Protein Req
- Waist
- Blood Pressure - three boxes are available for documenting subsequent readings.
Diabetes Mellitus - check boxes are present for indicating whether or not the patient has diabetes.
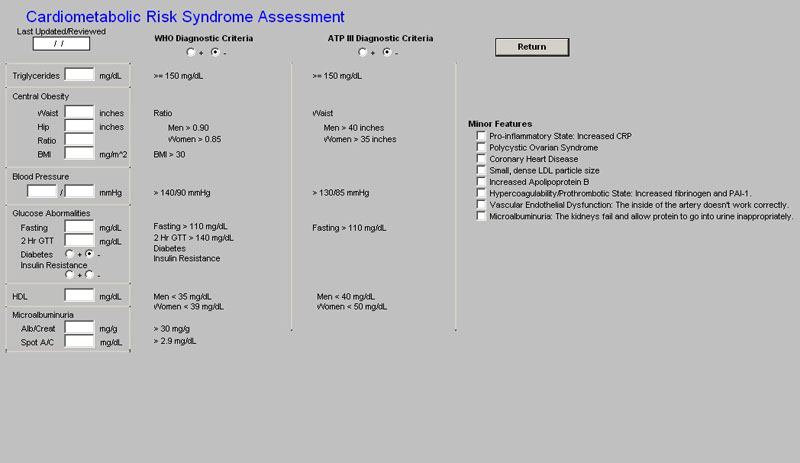
Metabolic Syndrome - this is a link to the assessment template for the Metabolic Syndrome. The elements of diagnosing the Metabolic Syndrome are automatically populated and the determination is made as to whether the patient has the Metabolic Syndrome or not. Both the World Health Organization and the ATP-III criteria are displayed, but the notation for the presence of the Metabolic Syndrome in SETMA's templates is based on ATP-III.
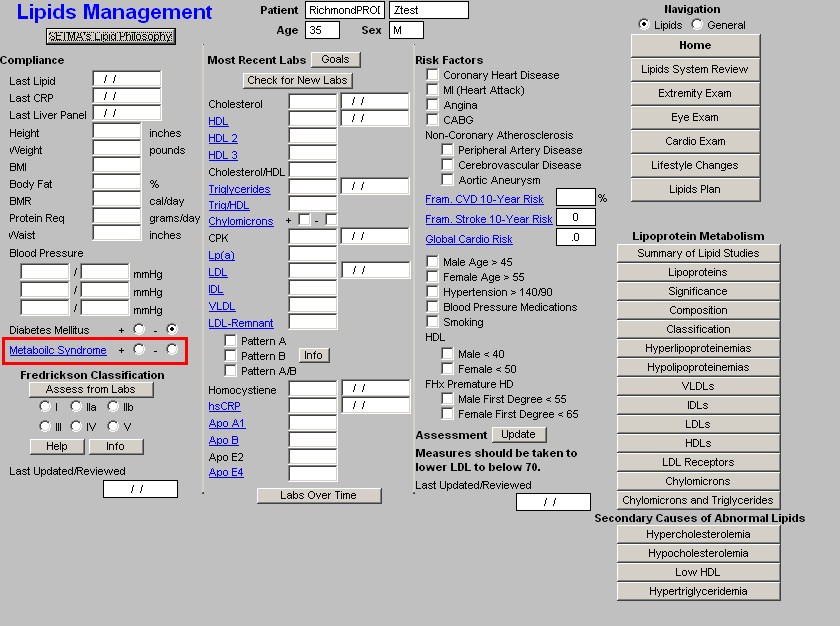
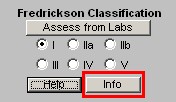
Fredrickson Classification
- Assess from Labs - this button (Assessment from Labs) launches a calculation which evaluates the laboratory data displayed in column 2 to determine which one of six Fredrickson Classes of Lipids is present in this patient. There are times, particularly when the patient is treated, that the classification will not automatically calculate. And, there are many times, of course, when the patient's lipids are normal and therefore the classification does not calculate because it does not apply.
- Types I, IIa, IIb, III, IV, V - when the Assess from Labs button is depressed and when there is a clear Fredrickson category present, the appropriate check box is automatically indicated
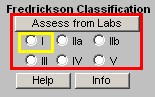
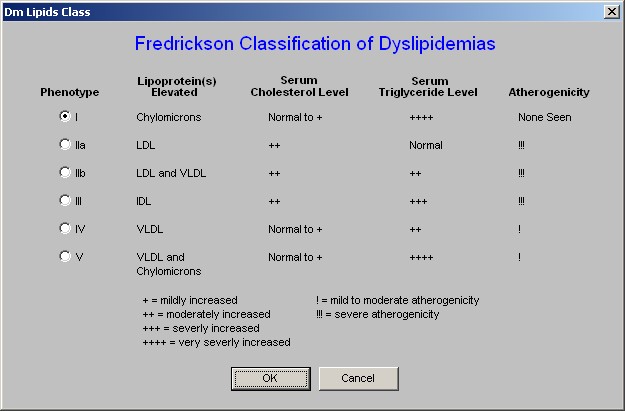
- Help - this help button launches a pop-up which displays the six Fredrickson
Classifications and gives the details of each based on:
- Lipoproteins Elevated,
- Serum Cholesterol Level,
- Serum Triglyceride Level.
- Atherogencicity.
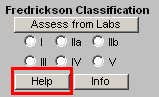
- Info - this button launches a monograph about the particular Fredrickson Classification which is indicated by the Assess from Lab function. This article can be printed and given to the patient or read by the provider.

Column 2 --
At the top, you will find the patient's name, age and sex
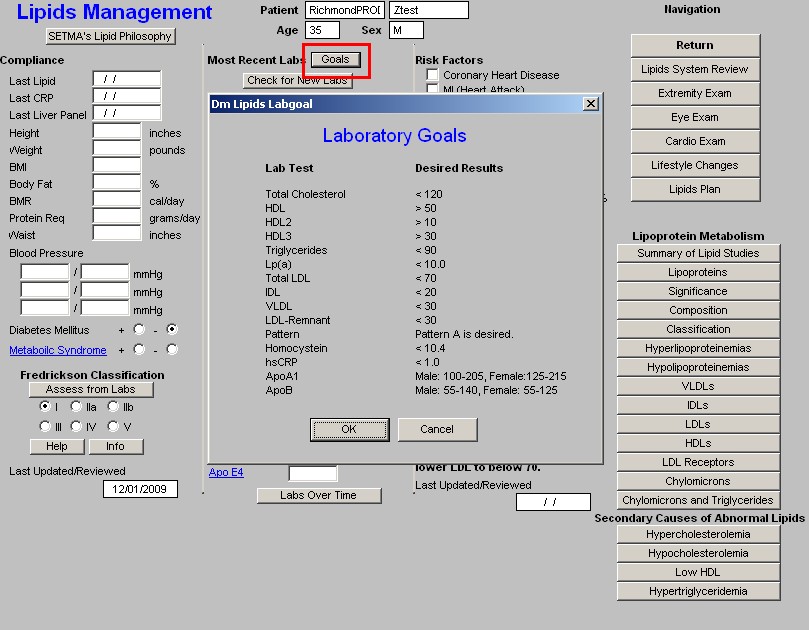
Beneath that is a button entitled "Goals," this gives SETMA's goals in treating . They are:
| Total Cholesterol | <120 |
| HDL | >50 |
| HDL2 | >10 |
| HDL3 | >30 |
| Triglycerides | <90 |
| Lp(a) | <10 |
| Total LDL | <70 |
| IDL | <20 |
| VLDL | <30 |
| LDL-Remnant | <30 |
| Pattern | Pattern A |
| Homocysteine | <10.4 |
| hsCRP | <1.0 |
| ApoA1 | Male 100-205; Females 125-215 |
| ApoB | Male 55-140; Females 55-125 |
These are aggressive goals but emerging research data is supporting these as appropriate goals for those who are either at "high risk" as determined by:
- the Framingham Risk Score,
- a personal history of cardiovascular disease,
- the presence of diabetes,
- having the metabolic syndrome
and/or
- a personal desire to eliminate atherosclerosis risk so far as is possible.
Beneath this is a button entitled "Check for new labs" - when this button is depressed the system finds the latest laboratory values available and populates the template with them. The date on which each lab test was performed is indicated in the box to the right of each lab value.
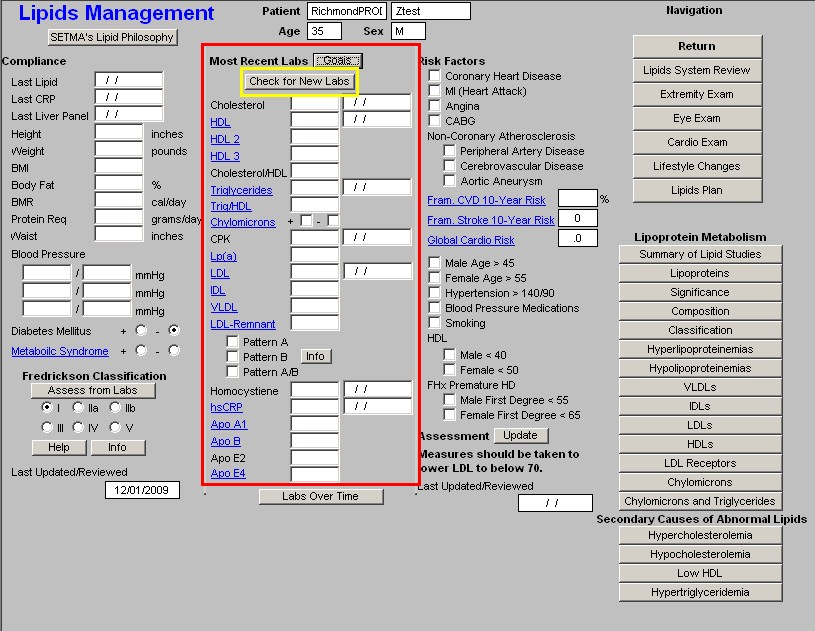
Note: Any Lab Name which is in Blue has a explanatory document attached to it which can be accessed by the clicking of the name. The document launched by these buttons can also be printed.

The lab results which are automatically pulled from NextGen's Laboratory Module into
SETMA's Master Lipid Template are:
- Cholesterol
- HDL
- HDL 2
- HDL 3
- Cholesterol/HDL Ratio
- Triglycerides
- Trig/HDL
- Chylomicrons
- CPK
- Lp(a)
- LDL
- IDL
- VLDL
- LDL-Remnant
- Pattern A
- Pattern B
- Pattern A/B
- Homocsyteine
- hsCRP
- ApoA1
- ApoB
- ApoE2
- Apo E4
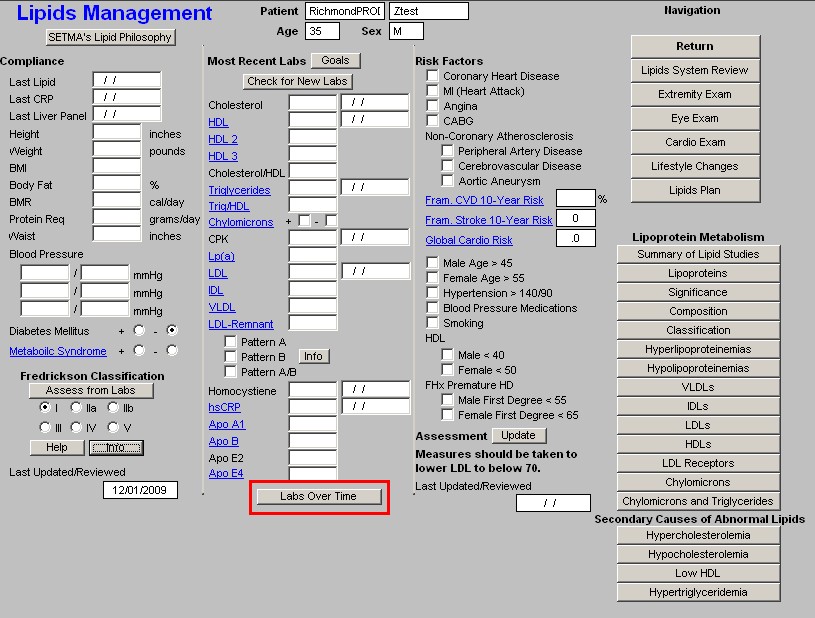
At the bottom of this column is a button entitled "Lab Over Time," which allows you to simultaneously view the results of multiple lab values on different dates.
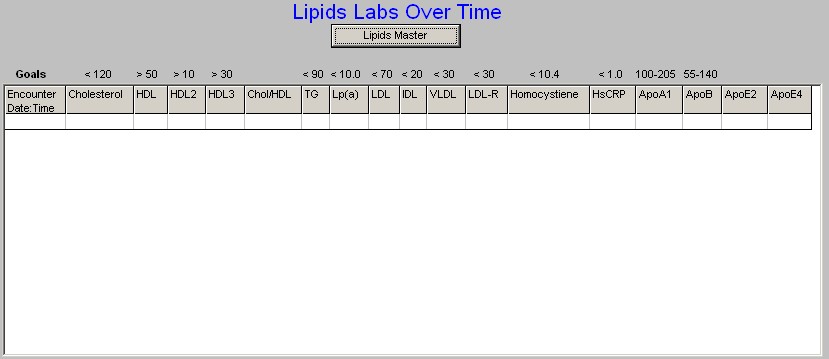
Note: The Menu Bar's File/Graph function allows you to display any lab value in graph form. For information on using this function go to the Tutorial on "How to Navigate within NextGen.
Column 3 --
Risk Factors - these, along with Diabetes and the Metabolic Syndrome, which are documented in column 1, identify the factors which increase the patient's risk of cardiovascular disease and consequently increases the need to control the patient's lipids aggressively. They are:
Note: If the Cardiac Hx data is properly filled out on the History template, this data will automatically populate. For details go review the Master GP Tutorial with particular attention to the History Template.
- Coronary Heart Disease
- MI (Heart Disease)
- Angina
- CABG
- Non-Coronary Atherosclerosis
- Peripheral Vascular Disease
- Cerebrovascular Disease
- Aortic Aneurysm
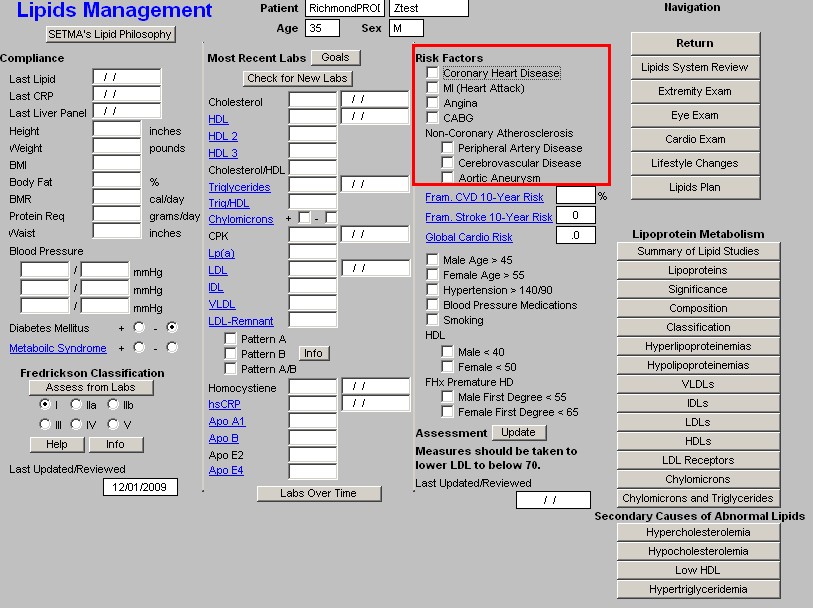
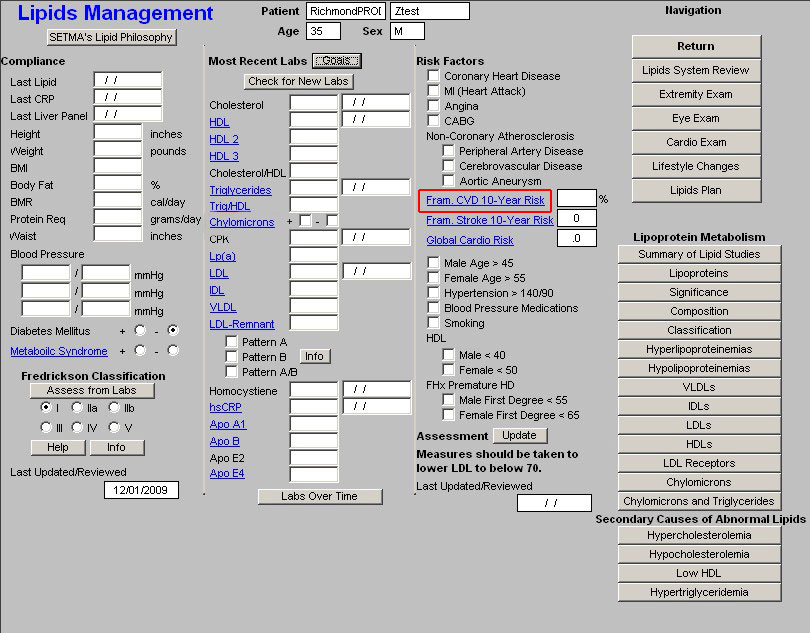
Beneath these Risk Factors are three links which evaluates the cumulative risk of a number of risk factors based on the Framingham Data:
Framingham 10-Year CVD Risk
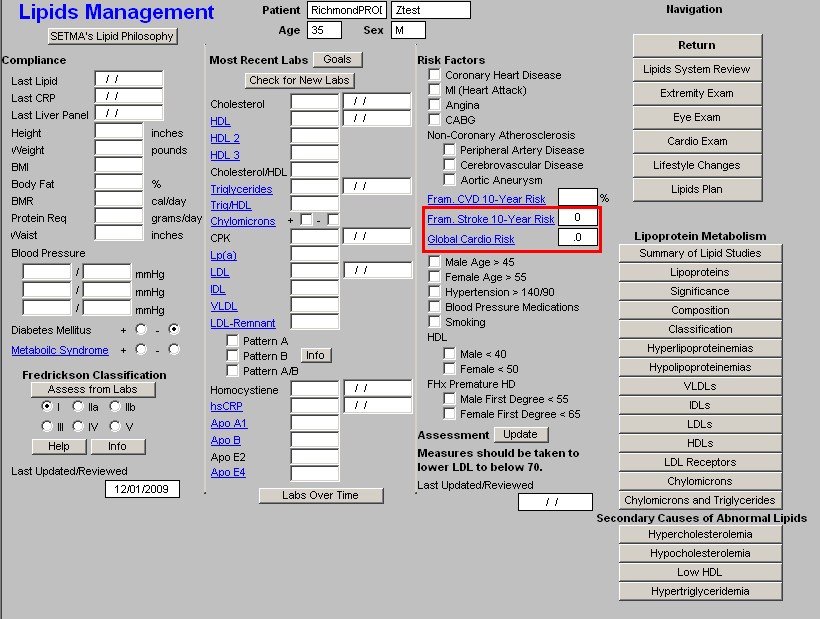
Framingham 10-year Stroke Risk
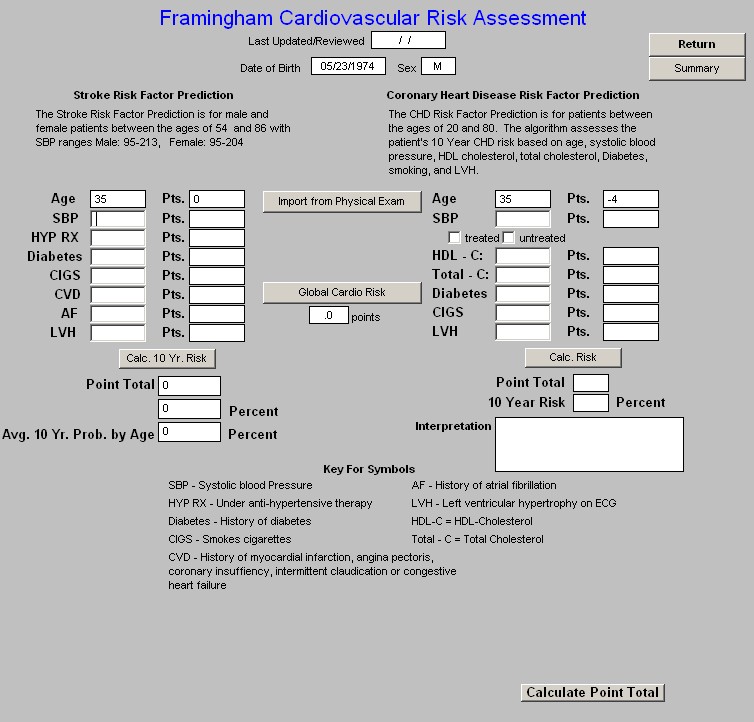
NOTE: Both of the above hyperlinks will access the "Framingham Cardiovascular Risk
Assessment" template.
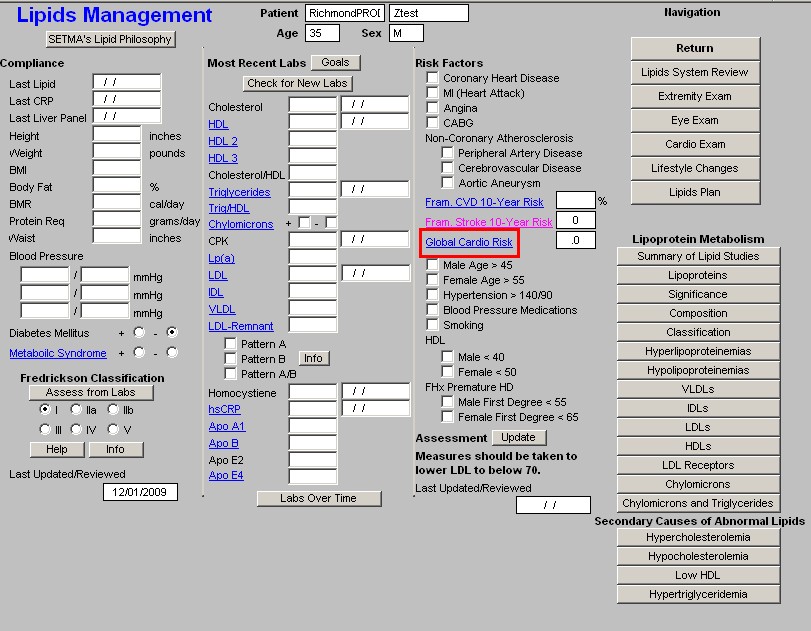
- Global Cardio Risk - this is a new calculation which is based on the Framingham Data but which only addresses the five modifiable risk factors. A score above 4 indicates an increased cardiovascular risk burden. The five modifiable risk factors are:
- Cholesterol
- HDL
- Hgb A1C
- Systolic Blood Pressure
- Smoking
Following the links to these three calculated cumulative risk scores are additional risk factors for cardiovascular disease:
- Male age over 55
- Female age over 65
- Hypertension (blood pressure over 140/90) - while a blood pressure of 140/90 is used as a "cut off" for assessing a patient with as being hypertensive, this is NOT the treatment goal for high risk patients. A blood pressure of 110/70 ought to be the goal for all patients with cardiovascular disease and with cardiovascular disease equivalents such as diabetes.
- Blood Pressure Medication - not only is the blood pressure over 140/90 a risk factor, but also treatment with blood pressure medication represents an additional risk factor which increases the necessity for aggressively treating lipids.
- Smoking -- for smoking cessation initiatives see tutorial on Smoking Cessation in the LESS Initiative tutorial.
- HDL
- FHx Premature Heart Disease - family history of premature heart disease
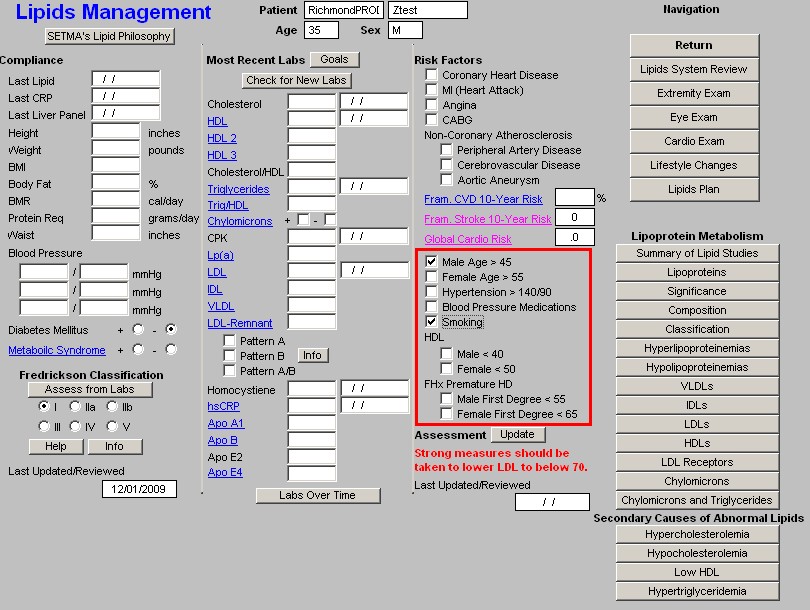
- Assessment - when the button next to Assessment, which is entitled "Update" is depressed, a conclusion will appear as to how aggressively the patient's lipids should be treated.
Column 4 -
This column has two sections organized from top to bottom.
Top Section of Column 4 - Navigation Buttons
There are two check boxes at the top of this list of Navigation Buttons. When the left check box entitled Lipids is activated, there will be a list of navigation buttons which take you through the lipid templates. They are:
- Home - this takes you back to AAA Home
- Lipids Review of Systems - this is a focused review of systems which is relevant to the treatment of Lipids. All of the fields in this Review of Systems interact with the Master GP Review of Systems.
- Extremity Exam - for details of this template see the tutorial for Master GP Extremity
Exam
- Eye Examination
- Cardio Exam
- Lifestyle changes
- Lipid Plan
For details on the Lipid Lifestyle Changes and Lipid Plan see below.
When the box next to General is activated, there will be a list of navigation buttons which take you though the Master GP Templates which are associated with Lipid Management. They are:
- Home
- Chief/chronic
- Histories
- Physical Exam
For how to use these templates see Master GP Suite of Templates tutorial under the name of each of these templates.
By switching back and forth from the Lipids and General set of templates, it is possible to complete an entire visit which is focused only on Lipids - a rare circumstance - from the Lipid Suite of templates.
Column 4 Section 2 -
The second section of column 4 of the Master Lipids Template is comprised of Educational materials on Lipids. The following will be found there:
- Lipoprotein Metabolism
- Summary of Lipid Studies -- "Lessons Learned from Recent Lipid-Lowering Trials: Why Physicians Should Change Clinical Practices." This is a summary of the six major lipid studies and what we have learned from them.
- Lipoproteins
- Significance - This launches and prints a document entitled, "Clinical Significances of Lipoprotein Metabolism."
- Composition
- Classification
- Hyperlipoproteinemias
- Hypolipoproteinemias
- VLDLs - This launches and prints a brief discussion of the origins and significance of Very
Low Density Lipoproteins.
- IDLs -- This launches and prints a brief discussion of the origins and significance of
Intermediate Density Lipoproteins.
- LDLs - This launches and prints a brief discussion of the origins and significance of Low
Density Lipoproteins.
- HDLs - This launches and prints a brief discussion of the origins and significance of High
Density Lipoproteins.
- LDL Receptors
- Chylomicrons -- This launches and prints an article entitled, "Exogenous Lipid Transport Pathway: Chylomicrons," which answers questions about the origin and significance of chylomicrons.
- Chylomicrons and Triglycerides - this document discusses the difference between chylomicrons and triglycerides.
Secondary Cause of Abnormal Lipids - these documents list the conditions which contribute to abnormalities of these four lipid abnormalities.
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Hypocholesterolemia
- Hypertiglyceridemia
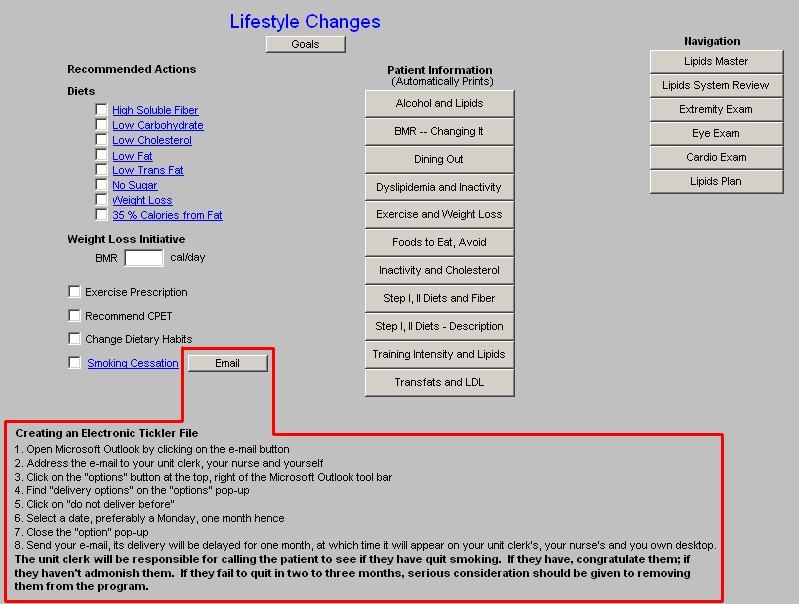
Lipids Lifestyle Changes Template
Without doubt, the first and most critical issue in lipid management is lifestyle modification. This template organizes the approach to those changes which will benefit lipid management.
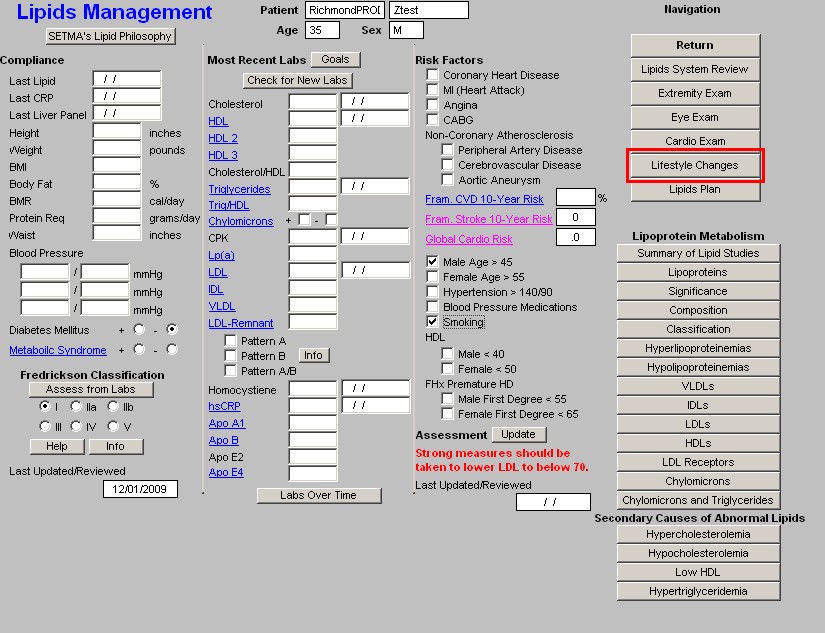
This template is organized into three columns.
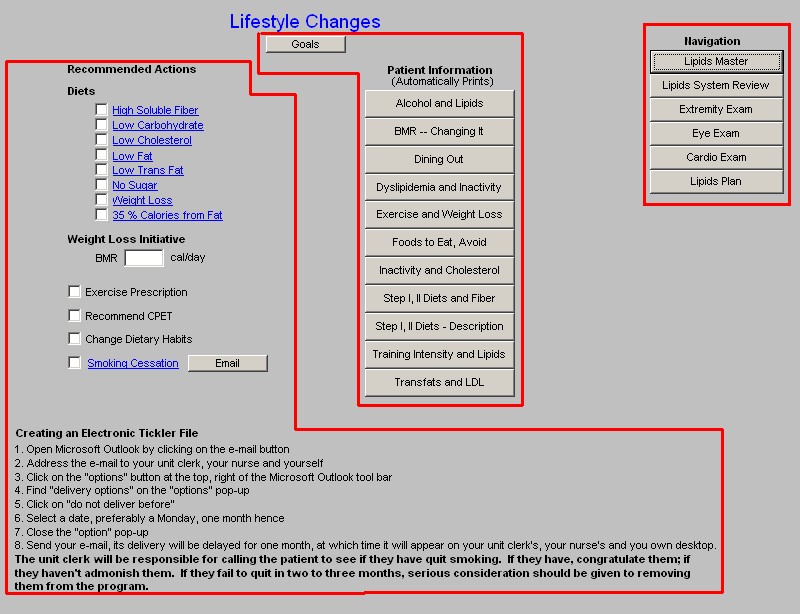
Column 1 - Recommended Actions
Diets - each of the below provides a patient-information document on the type of diet named.
- High Soluble Fiber
- Low Carbohydrate
- Low Cholesterol
- Low Fat
- Low Trans Fat
- No Sugar
- Weight Loss
- 35% Calories from Fat
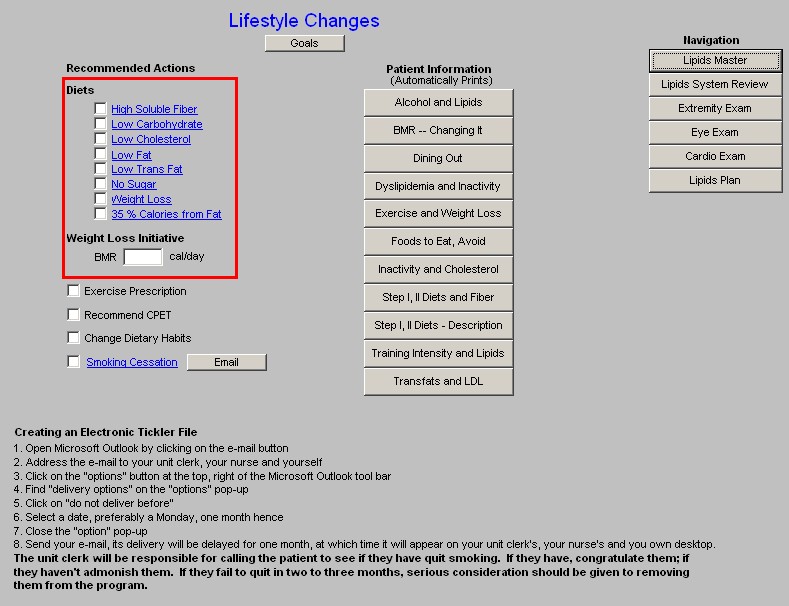
Weight Loss Initiative - any initiative in treating lipid abnormalities must include weight reduction. Below are elements of weight management in any patient.
- Exercise Prescription - this is a link to the exercise prescription. A weight management effort without consistent structured exercise and/or life-style changes which result in increased activity WILL NOT be successful.
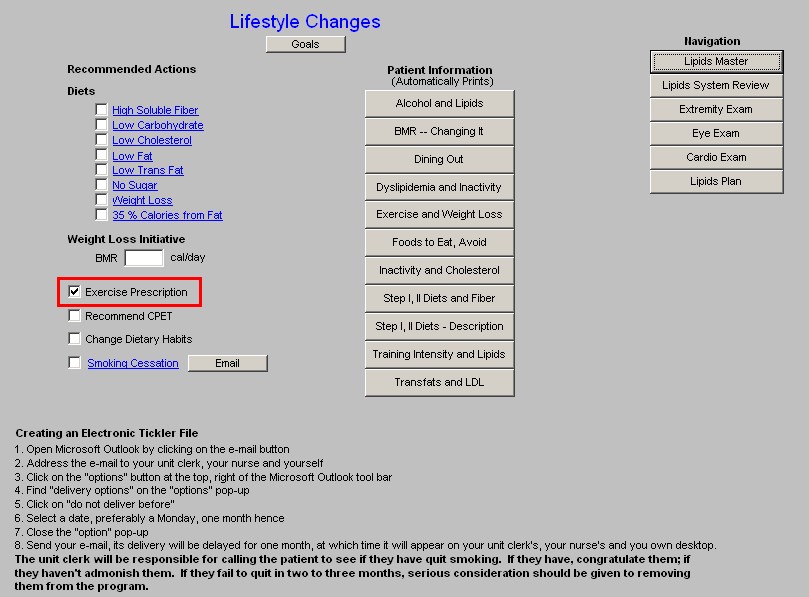

- Recommended CPET - Cardiopulomary Exercise Testing is a key element of prescribing a proper exercise program for any patient. CPET distinguishes between shortness of breath which is due to coronary artery disease, pulmonary disease and/or deconditioning. It should be a starting point for improving the overall health of any patient who is over 40.
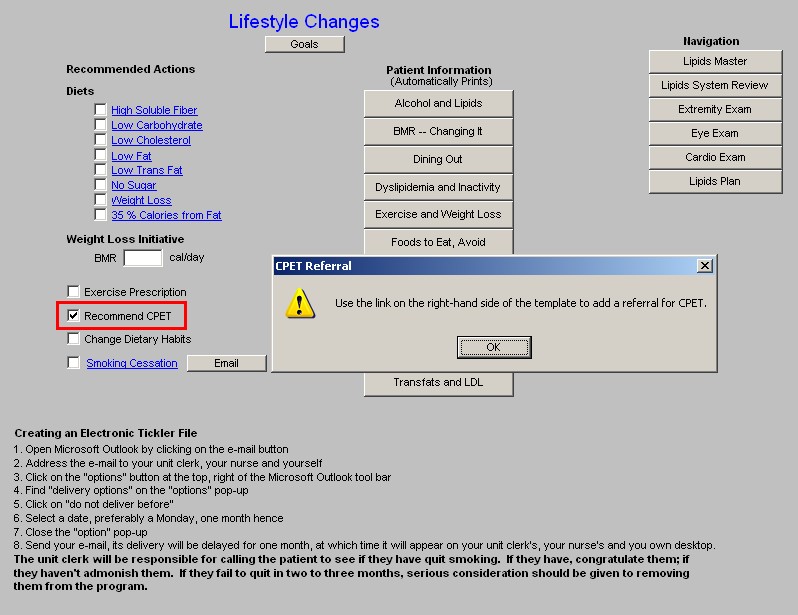
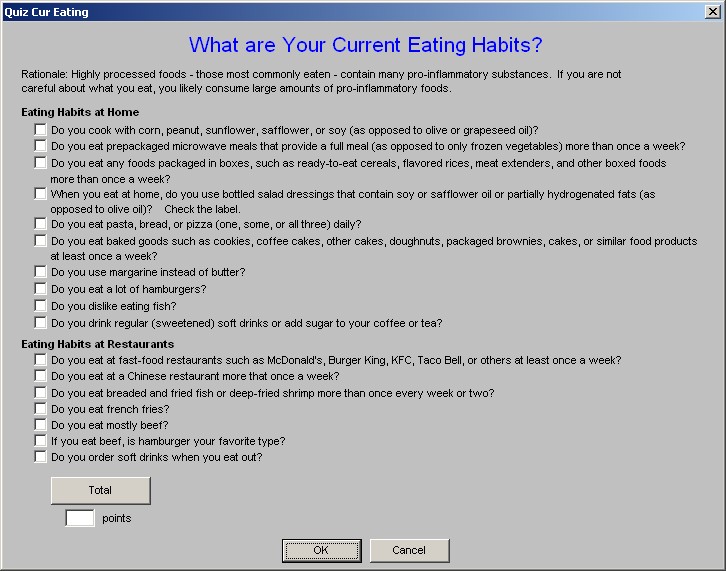
- Change Dietary Habits - this is a check box to document that you have discussed dietary changes with the patient. If the hyperlink is clicked, a template entitled "What are Your Current Eating Habits?" will be launched.
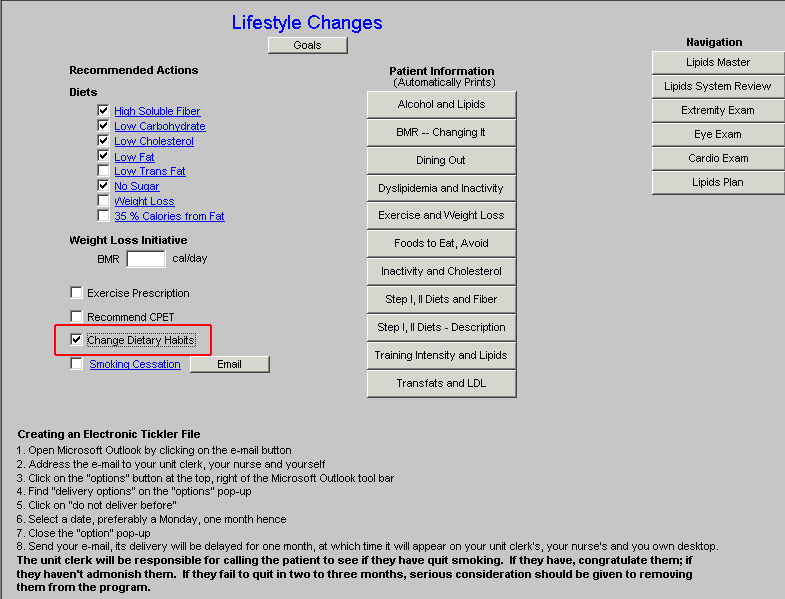
NOTE: When this template is completed it will provide a risk score for the potential of inflammation in the body.
- Smoking Cessation - lipid management without smoking cessation will not significantly improve a patient's cardiovascular risk profile.
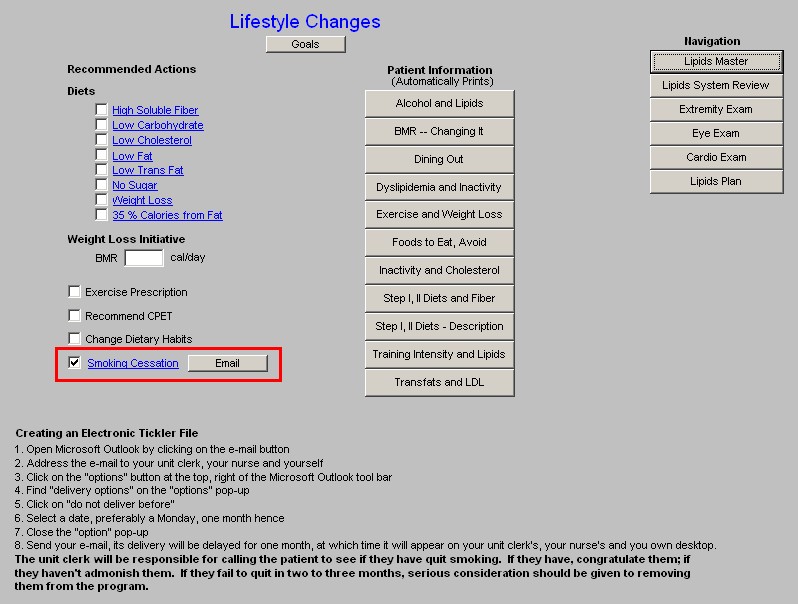

- E-Mail - this button launches a preprogrammed e-mail which provides follow-up instructions for a patient who is attempting to stop smoking.
- Creating an Electronic Tickler File - this gives instructions of how to create an electronic tickler file.
Column 2 -
Goals - this button launches a pop-up with the following information:
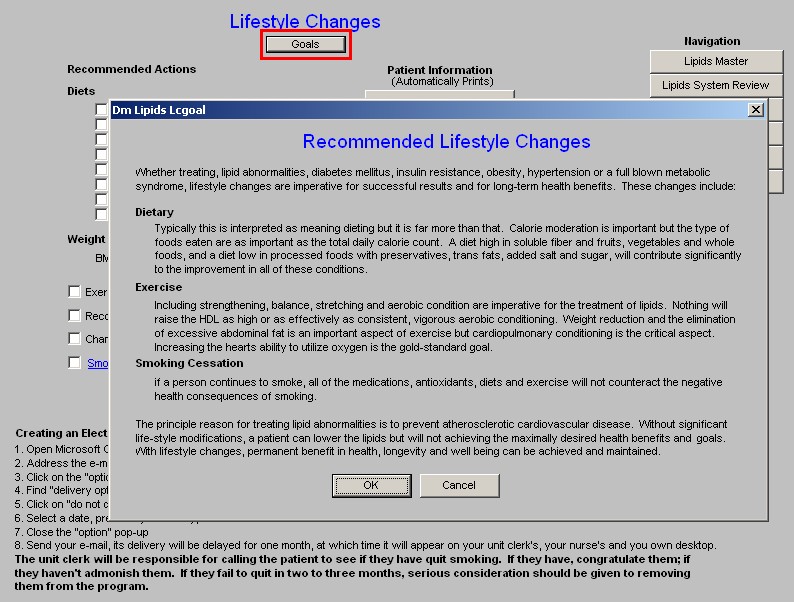
Whether treating, lipid abnormalities, diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance, obesity, hypertension or a full blown metabolic syndrome, lifestyle changes are imperative for successful results and for long- term health benefits. These changes include:
Dietary
Typically this is interpreted as meaning dieting but it is far more than that. Calorie moderation is important but the type of foods eaten are as important as the total daily calorie count. A diet high in soluble fiber and fruits, vegetables and whole foods, and a diet low in processed foods with preservatives, trans fats, added salt and sugar, will contribute significantly to the improvement in all of these conditions.
Exercise
Including strengthening, balance, stretching and aerobic condition are imperative for the treatment of lipids. Nothing will raise the HDL as high or as effectively as consistent, vigorous aerobic conditioning. Weight reduction and the elimination of excessive abdominal fat is an important aspect of exercise but cardiopulmonary conditioning is the critical aspect. Increasing the hearts ability to
utilize oxygen is the gold-standard goal.
Smoking Cessation
If a person continues to smoke, all of the medications, antioxidants, diets and exercise will not counteract the negative health consequences of smoking.
The principle reason for treating lipid abnormalities is to prevent atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Without significant life-style modifications, a patient can lower the lipids but will not achieving the maximally desired health benefits and goals. With lifestyle changes, permanent benefit in health, longevity and well being can be achieved and maintained.
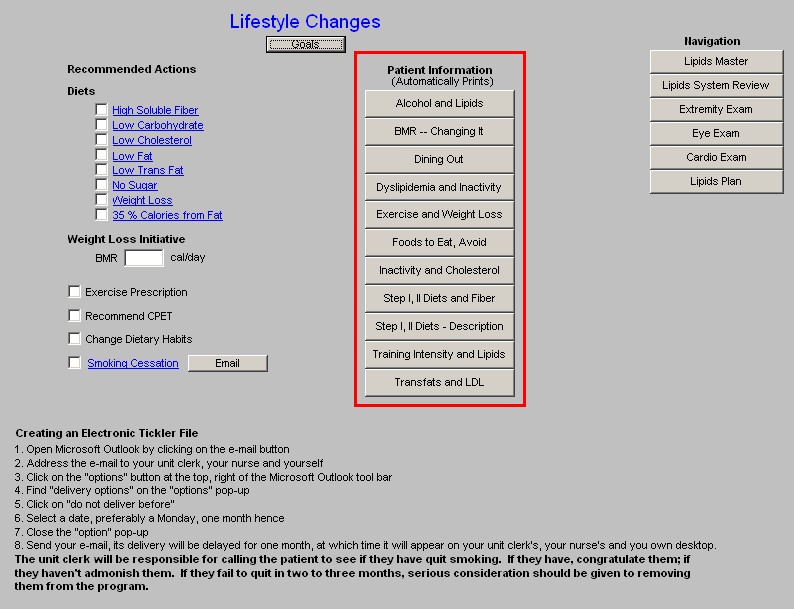
Patient information - these documents provide helpful information to patient's as to steps they can take to improve their lipid profiles.
- Alcohol and Lipids
- BMR - Changing It
- Dining Out
- and Inactivity
- Exercise and Weight Loss
- Foods to Eat, Avoid
- Inactivity and Cholesterol
- Step 1, II Diets and Fiber
- Step 1, II Diet - Description
- Training Intensity and Lipids
- Transfats and LDL
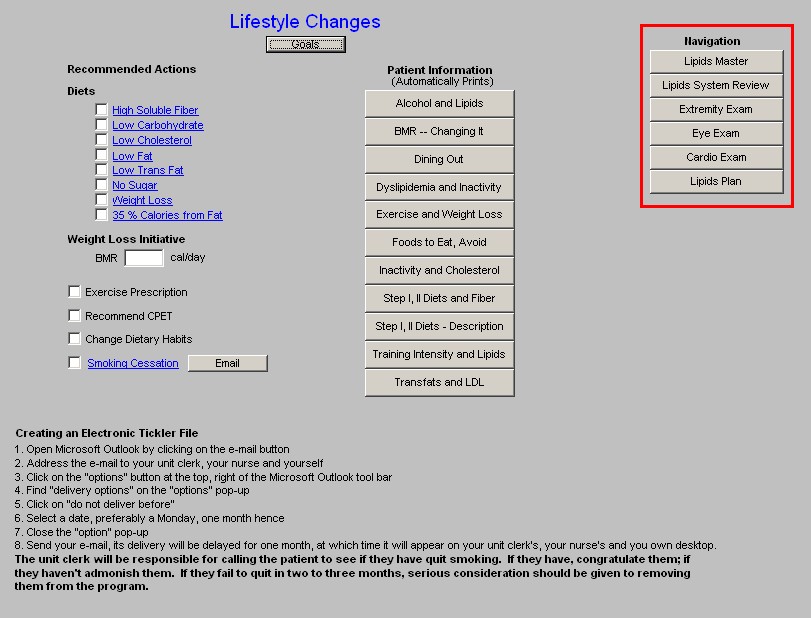
Column 3 -
Navigation Buttons - these buttons allow you to move easily within the Lipid Suite of Templates.
- Lipid Master
- Lipids Systems Review
- Extremity Exam
- Eye Exam
- Cardio Exam
- Lipids Plan
- Referral for CPET - this function allows you to refer the patient for a CPET from the Lipid
Lifestyle Changes template.
Lipid Plan Template
This template is organized into three columns. It provides a guide and a summary to the strategy for comprehensive management of a patient's lipids.
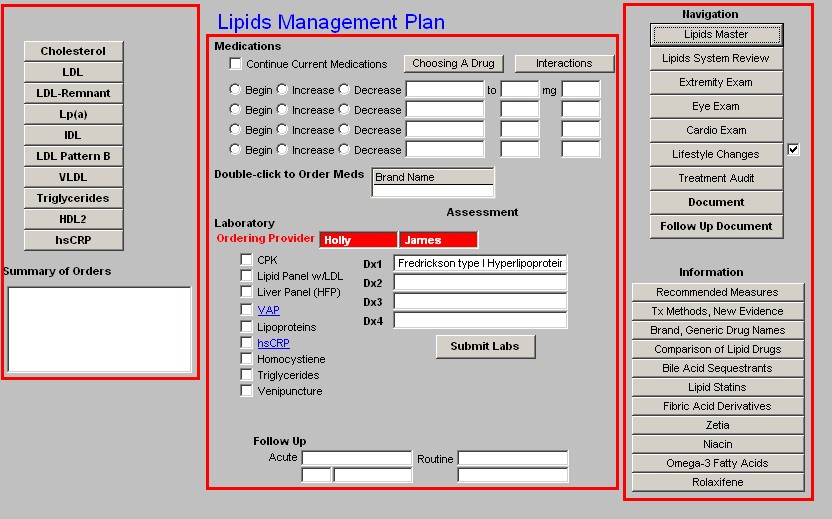
Column 1 -
This column provides treatment recommendations for the following Lipid particles and/or components of the lipid evaluation:
- Cholesterol - when either the Cholesterol or the LDL button is depressed, a pop-up appears with the following information:
- Across the top the patient's lab values for LDL, HDL, Triglycerides and non-HDL Cholesterol appear.
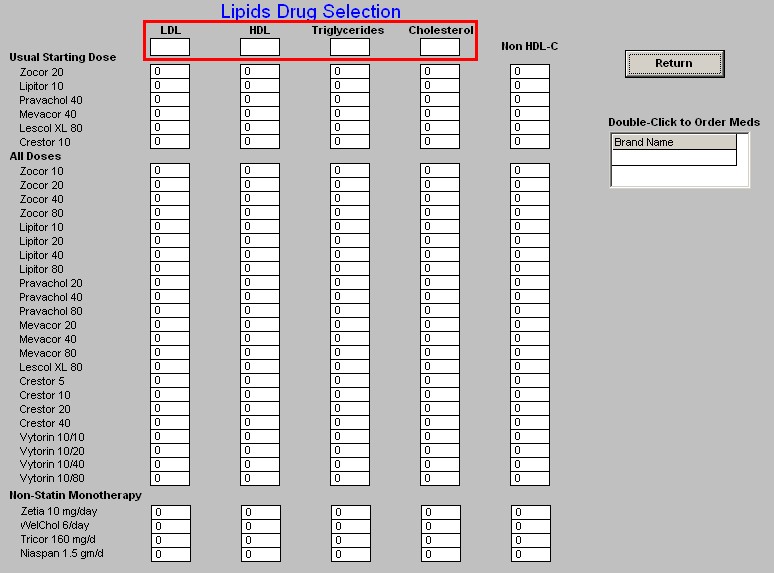
- Down the left side is a list of all of the cholesterol-lowering medications which are presently on the market.
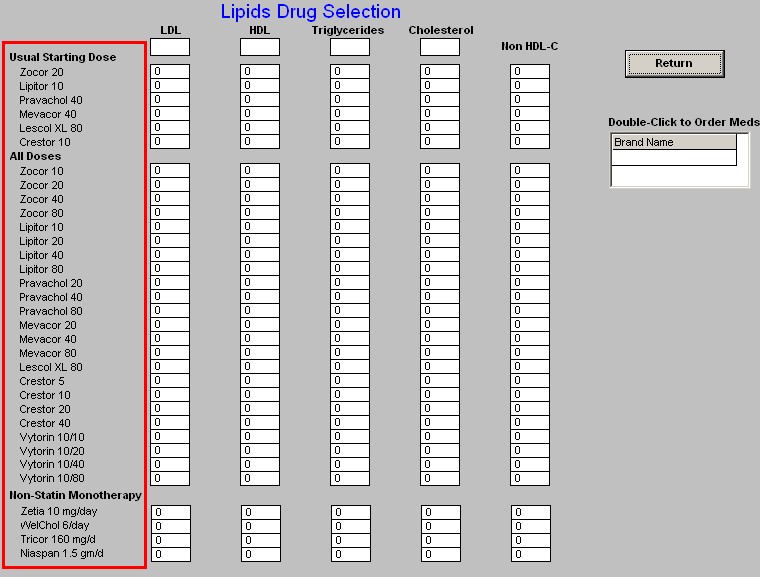
- In a table format the expected results for each of the elements of the lipid evaluation appear.
- This allows you to choose a medication which will get you to the patient's lipid goals based on SETMA's treatment goals.
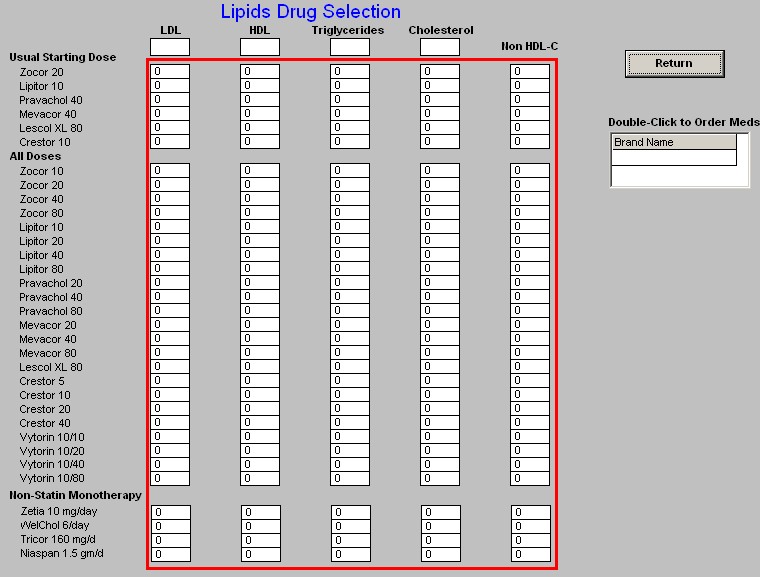
- There is also a link which carries you to NextGen's Medication module in order to order medication from this pop-up.
Return - this button appears just above the Medication Module link and when depressed carries you back to the Lipid Plan Template.
LDL - see Cholesterol above, as this button functions in the same way.
LDL-Remnant - this button launches a pop-up with the title LDL-Remnant Correction
Measures. It contains the following:
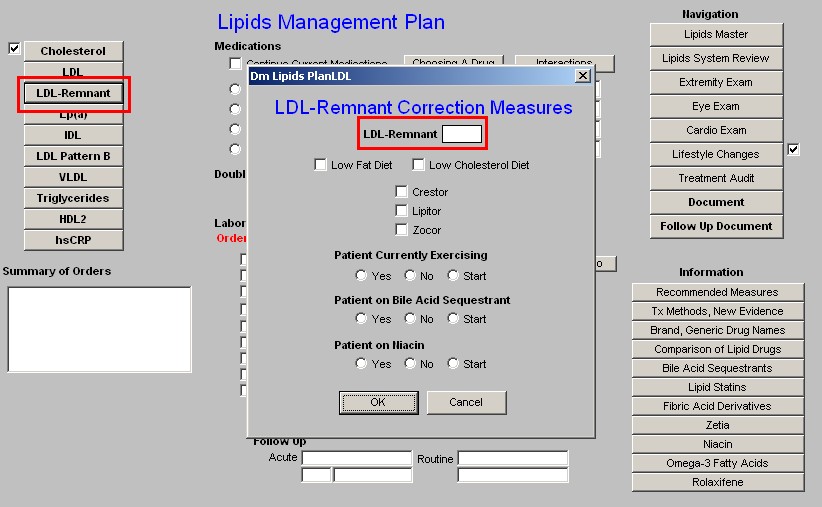
1. LDL-Remnant - this is a box where the laboratory result for this lipid particle appears if it is present in the system.
- For an explanation of the LDL-Remnant, go to the Master Lipid Template and click on the name LDL-Remnant.
- This will launch a brief document which explains the importance of this Lipid particle.
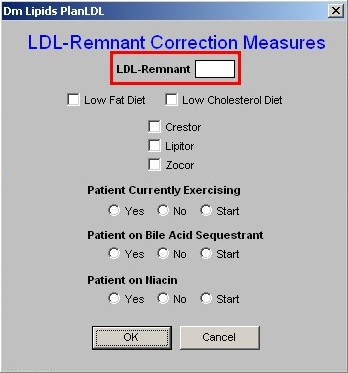
2. Low Fat Diet - the only two dietary interventions which affect the LDL-Remnant specifically are the Low Fat Diet and the Low Cholesterol Diet.
- Checking the box next to Low Fat or Low Cholesterol will document that you are placing the patient on either or both of these diets.
- It will also check the same on the Life-Style Changes Template.
- Either of both diets should then be printed and given to the patient.
- Either diet is printed from the Life-Style Changes Template.
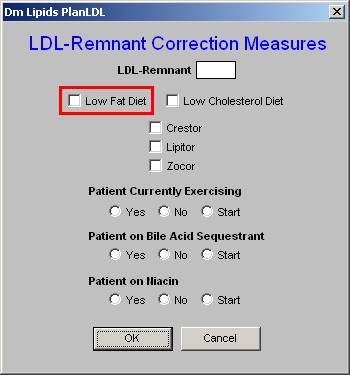
3. Low Cholesterol Diet - See the explanation above on the Low Fat Diet.
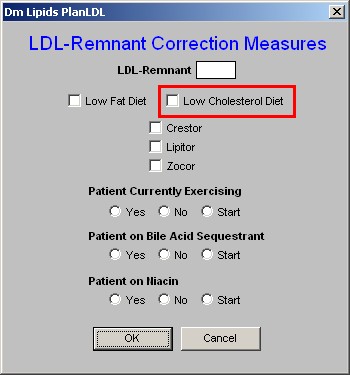
4. Crestor - There are only three statins which address the LDL-Remnant and they are Crestor, Lipitor and Zocor.
- If you elect to start the patient on Crestor, Lipitor or Zocor, there are two more actions which you need to take.
- One is to enter the medication in the space provided in the second column on the Lipid Plan template (see below).
- The other is to access the Medication Module from the Lipid Plan template and order the medication.
- Lipitor - see the explanation above for Crestor.
- Zocor - see the explanation above for Crestor.
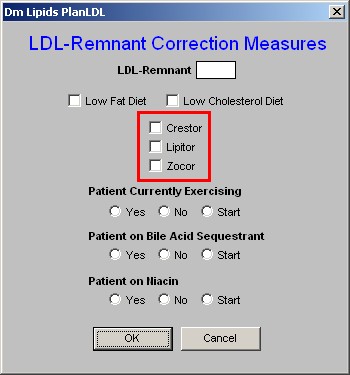
5. Patient Currently Exercising - Exercise is a critical element of treatment of any and all lipid abnormalities. - Here there are check boxes for "yes," "no," and "start."
- It is desirable to document the type, frequency and intensity of exercise which the patient is performing.
- This can be done from the Life-Style Template with its link to the Exercise template.
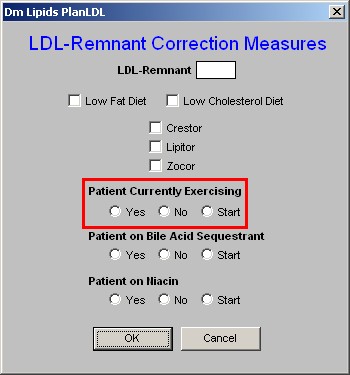
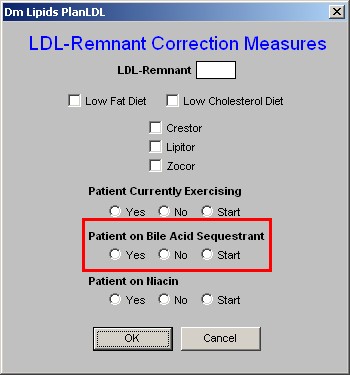
6. Patient on Bile-Acid Sequestrant - this is the second class of medications which affect the LDL-Remnant particle in lipids.
- There are check boxes for "yes,"no" or "start."
- If you elect to start the patient on a bile-acid sequestrant, there are two more actions which you need to take.
- One is to enter the medication in the space provided in the second column on the Lipid Plan template (see below).
- The other is to access the Medication Module from the Lipid Plan template and order the medication.
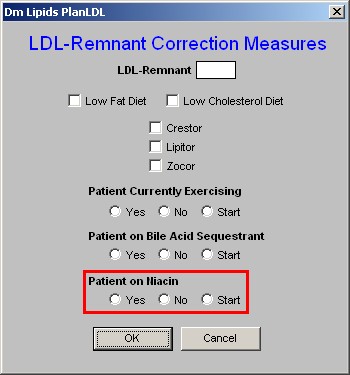
7. Patient on Niacin - this is the third class of drugs which affects the LDL-Remnant.
- There are check boxes for "yes," "no," or "start."
- If you elect to start the patient on Niacin, there are two more actions which you need to take.
- One is to enter the medication in the space provided in the second column on the Lipid Plan template (see below).
- The other is to access the Medication Module from the Lipid Plan template and order the medication.
- OK - this button saves your entries on this pop-up and closes the pop-up returning you to the Lipid Plan template.
- Cancel - this button cancels your entries on this template
-
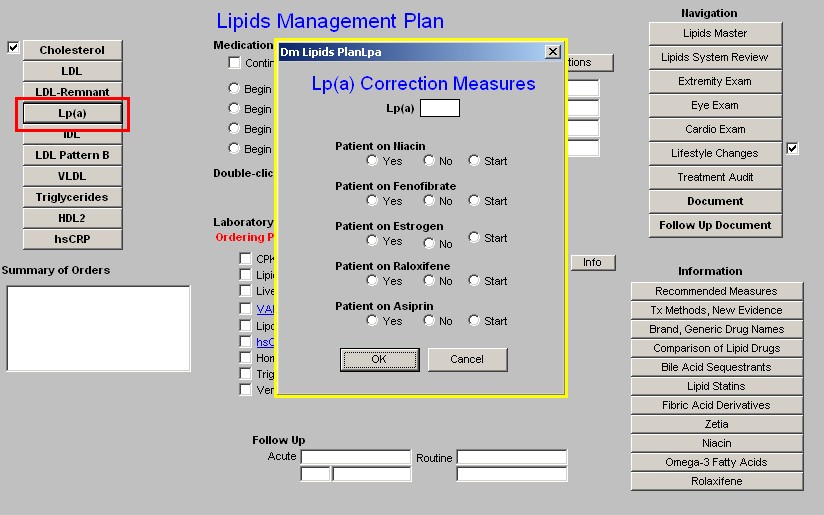
Lp(a) - this is pronounced "Lp little a." Information on its significance can be found by launching the document attached to the name Lp(a) on the Master Lipid Template.
- On the Lipid Plan template depressing the button entitled Lp(a) launches a pop-up entitled Lp(a) Correction Measures.
- There are five sets of checkboxes labeled "yes - no - start."
- As above, if any of these medications are chosen, they need to be entered into column 2 of the Lipid Plan Template (see below) and on the Medication Module.
- The five medications which improve Lp(a) are:
- Niacin
- Fenofibrate
- Estrogen
- Rolaxifine
- Aspirin
- IDL - this button launches a pop-up entitled IDL Correction Measures. It provides the following information and options:
- The value for the IDL if it exists in SETMA's lab system.
- Check box for a Low Carbohydrate Diet
- Patient Currently Exercising -- Check box for "yes," "no," or "start." Again, documentation of the patient's type, duration, frequency and intensity of exercise is available on the Exercise template which is launched from the Lipid's Lifestyle Changes Template.
- Patient on Statin - with a check box for "yes," no," or "start."
Note: If the patient is on a statin or if a statin is started a box will appear which asks if the patient is on Co Enzyme Q 10 (CoQ 10) or not. All patients who on a statin would benefit from CoQ10 treatment as the statins significantly decrease this very important naturally occurring enzyme.
- Patient on Niacin
- Patient on Fenofibrate
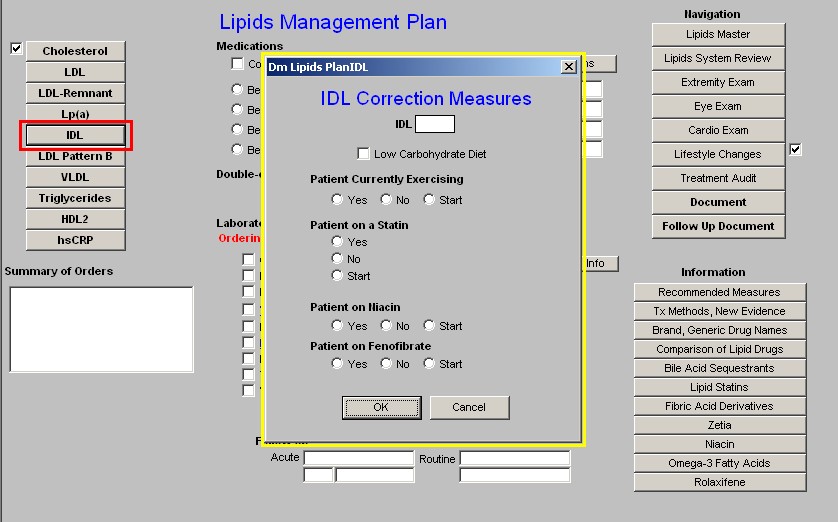
Note: If any or all of these medications are started, they should be entered in Column 2 of the
Lipid Plan template and in the Medication Module as well.
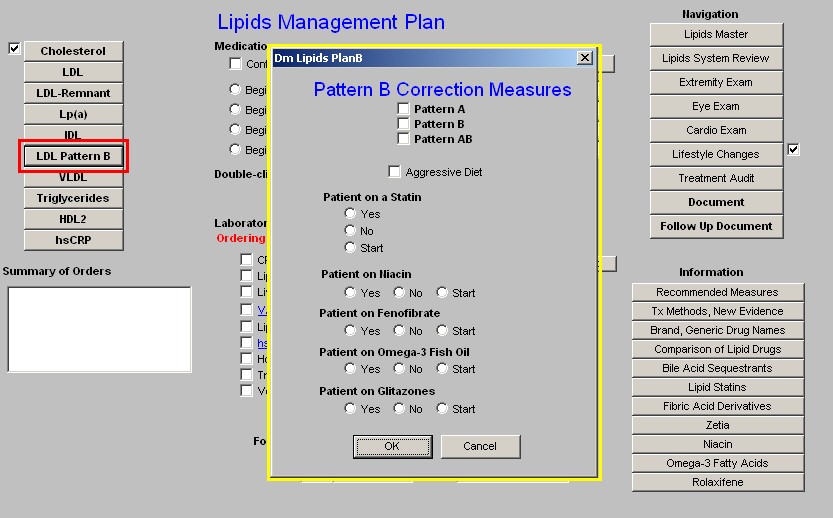
- LDL Pattern B - this launches a pop-up entitled Patten B Correction Measures. The pop-up provides the following information and options:
- The laboratory results of whether the patient has:
- Pattern A (desirable),
- Pattern B (undesirable) or
- Pattern A/B (mixed).
Note: More information on these patterns can be found from the education information available on the Master Lipid Template (see above) or elsewhere on the Lipid Plan Template (see below).
- Aggressive diet
- Statin
- Nicacin
- Fenofibrate
- Omega-3 Fish Oil
- Glitazones
VLDL -- this launches a pop-up entitled VLDL Correction Measures. The information and options include:
- VLDL lab results if available.
- Low Carbohdrate diet
- Exercise
- Statin
- Niacin
- Fenofibrate
- Omega 3 Fish Oil
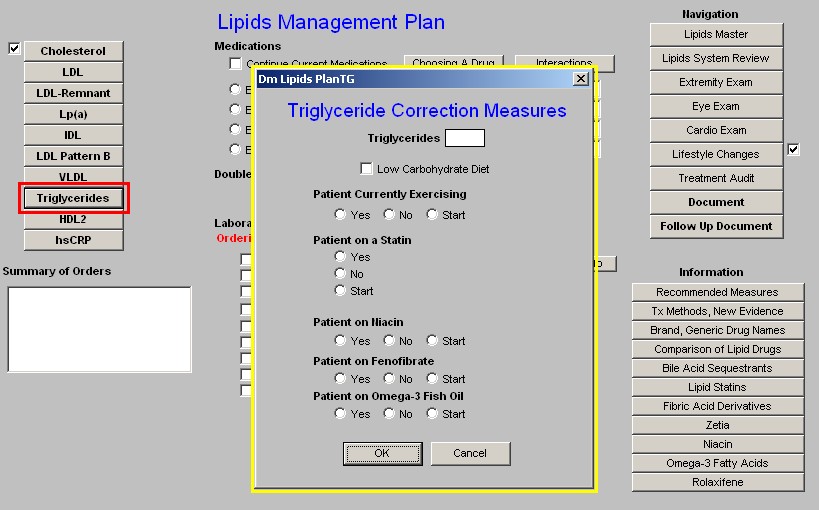
Triglycerides
- Triglycerides lab results.
- Low Carbohydrate diet - this is the most important aspect of treating triglycerides.
- Exercise
- Statin
- Niacin
- Fenofibrate
- Omega 3 Fish Oil

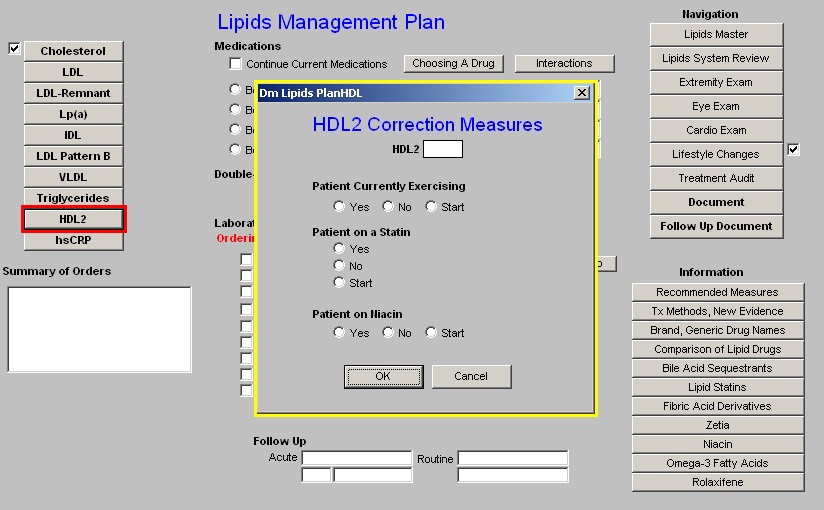
HDL2
- HDL2 lab results if available
Note: In the face of a low total HDL, even if the HDL2 and HDL 3 have not been measured, the treatment recommendations for low HDL2 apply.
- Statin
- Niacin
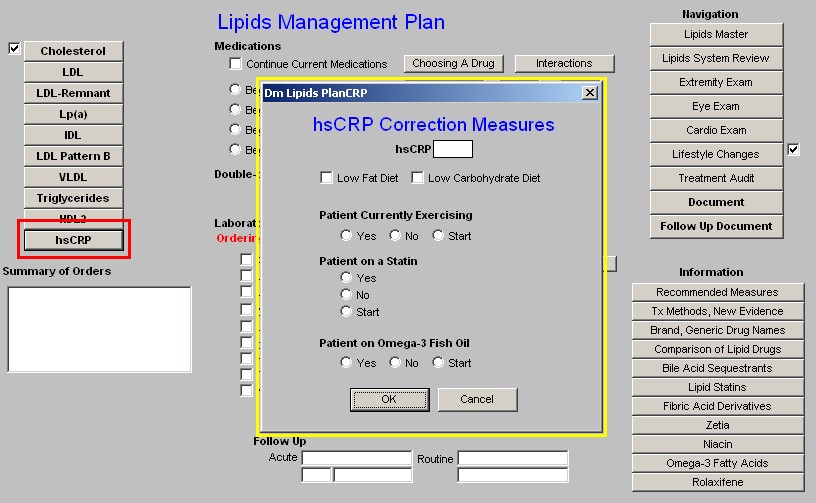
hsCRP
- hsCRP lab results
- Low Fat
- Low Carbohydrate Diet
- Exercise
- Statin
- Omega-3 Fish Oil
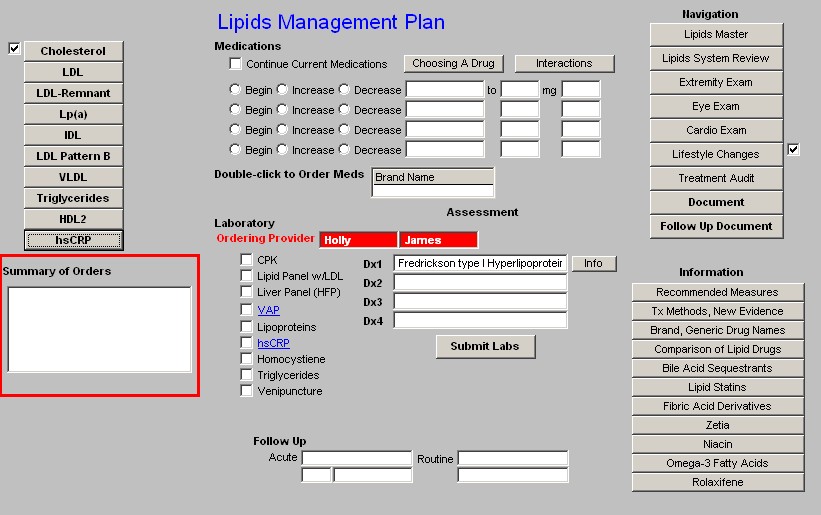
Summary of Orders
In this box, all treatment options which have been selected in the nine Correction Measures pop-ups above are summarized. Once all initiatives are determined, they should be documented in column 2, if medications, ordered in the Medication module and instructions given to the patient and/or to the unit clerk or nurse to give to the patient.
Column 2 - Medications -
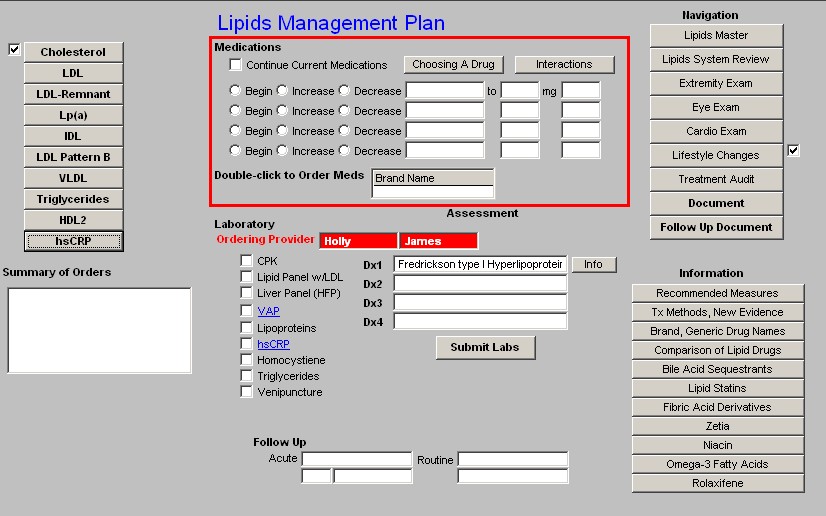
- Continue Current Medications - this check box allows you to continue present medications.
- Choosing a medication - this launches the same pop-up as on the links to Cholesterol
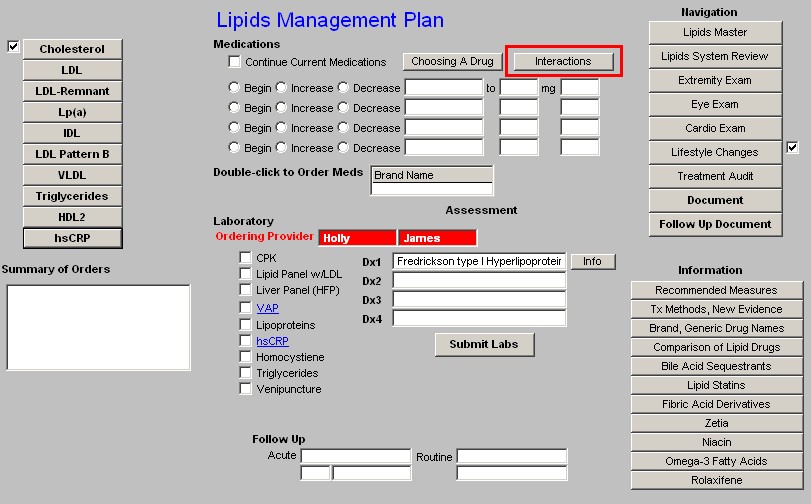
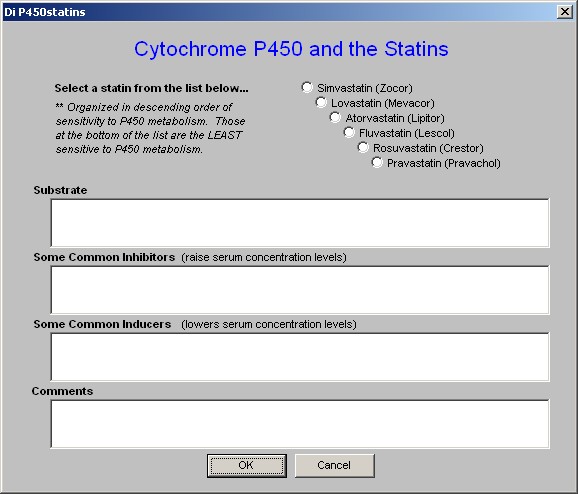
- Interactions - the growing number of drugs which are influenced by the Cytochrome P450 system makes it important for all providers to be able to easily review these interactions. It is impossible to know and/or remember all of this data. This function allows you to review it on line and in the midst of a patient encounter.
- This button launches a template entitled "Statins and Cytochrome P450," which is a part of the Drug Interactions material which is found on the second line of AAA Home.
- The link on Lipid Plan, displays the Cytochrome P450 material which relates specifically to statins.
- The six statins listed are in descending order of sensitivity to the P450 system.
- When accessed, this function allows for the selection of the statin of interest.
- The following information is then given on the selected statin:
- Substrate - this identifies the P450 enzyme which affects this statin.
- Common Inhibitors - this identifies the drugs and/or substances which decrease the activity of the P450 enzyme and which therefore increases the blood levels of this statin and which therefore can cause toxicity.
- Common Inducers - this identifies the drugs an/or substances which increase the activity of the P450 enzyme and which therefore decreases the blood levels of this statin and which can therefore cause the drug to be ineffective.
- Comments - this gives additional information about the impact of the P450 enzymes on this statin.
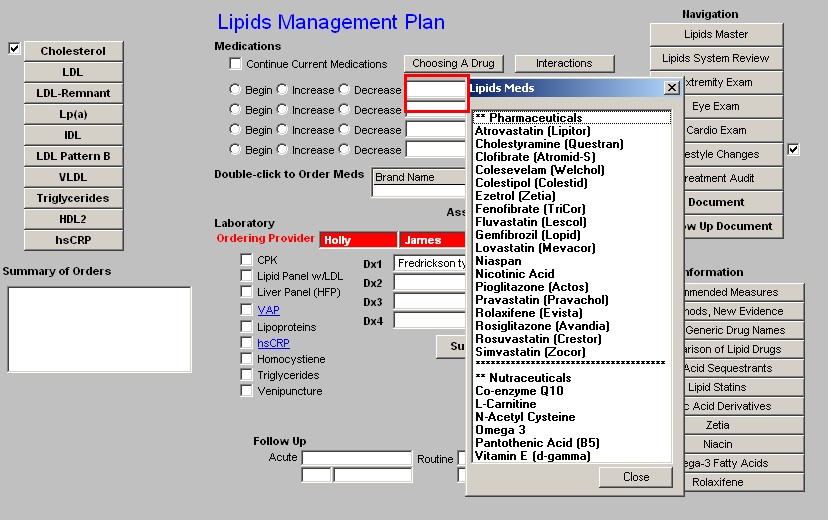
The next function in Column 2 is four sets of boxes for the beginning, increasing or decreasing of Lipid-related medications. The pick list for these boxes includes both pharmaceuticals and relevant Nutraceuticals.
Pick List
** Pharmaceuticals Atrovastatin (Lipitor) Cholestyramine (Questran) Clofibrate (Atromid-S) Colesevelam (Welchol) Colestipol (Colestid) Ezetrol (Zetia)
Fenofibrate (TriCor) Fluvastatin (Lescol) Gemfibrozil (Lopid) Lovastatin (Mevacor) Niaspan
Nicotinic Acid Pioglitazone (Actos) Pravastatin (Pravachol) Rolaxifene (Evista) Rosiglitazone (Avandia) Rosuvastatin (Crestor) Simvastatin (Zocor)
** Nutraceuticals
Co-enzyme Q10
L-Carnitine
N-Acetyl Cysteine
Omega 3
Pantothenic Acid (B5) Vitamin E (d-gamma) Cholifibrate (Atromid-S)
Space is provided for providing the name of the pharmaceutical and/or Nutraceuticals, the dosage and the frequency of dosing.
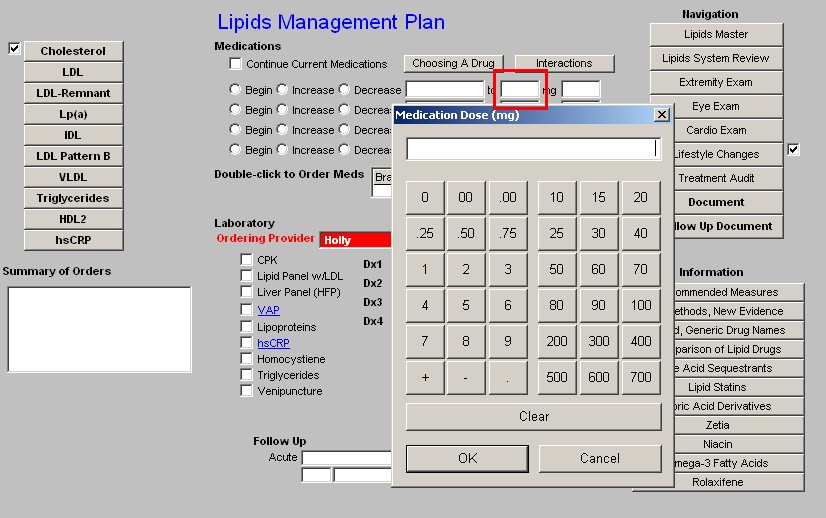
Beneath these four sets of boxes is a link to the medication module so that medications which are recommended can easily be ordered and placed in the patient's medication list.
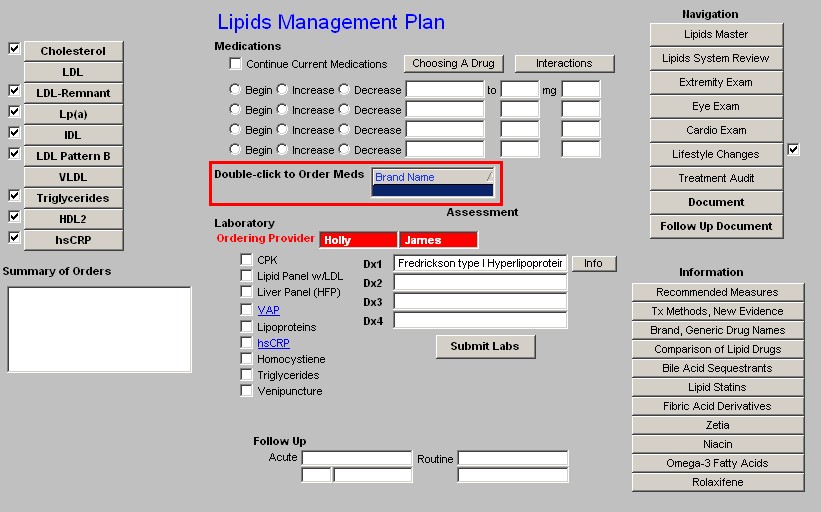
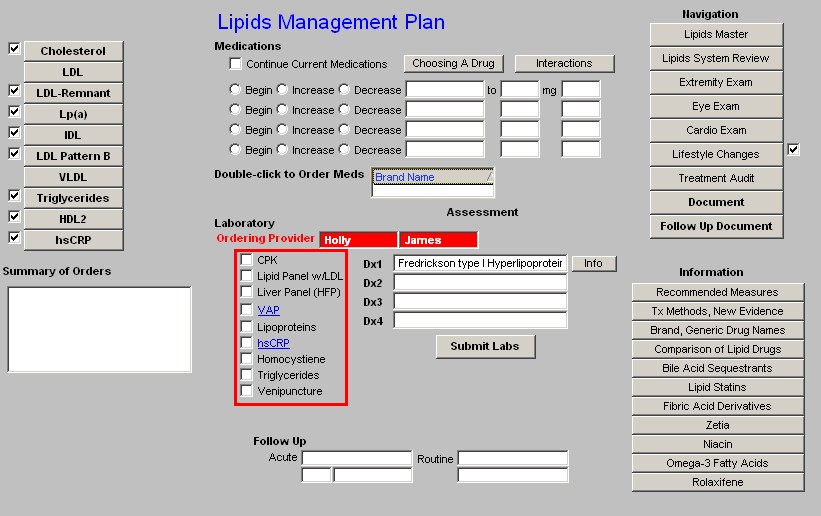
Beneath the link to the Medication module is a list of the Laboratory tests which can be ordered and charge posted from the Lipid Templates; they are:
- CPK
- Lipid Panel
- Liver Panel (HFP)
- VAP - when this option is selected, the five options which follow it are automatically checked as they are part of that evaluation. Remember, few insurance companies pay for a VAP although it is a very important part of a thorough Lipid evaluation.
- Spectophotometry
- Lipoproteins
- hsCRP
- Homocystiene
- Triglycerides
Next to the laboratory tests which can be ordered, are four Assessment boxes in which the patient's diagnosis can be documented.
- Because this is a special tool, it is possible to associated more than one name with each ICD-9 code and still have it work with charge posting.
- Therefore, in the first two Assessment boxes you will see diagnoses that are only related to lipids. All of these lipid ICD-9 codes which are not available from SETMA's ICD-9 Code list which is associated with the Dx3 and Dx4 Assessment boxes.
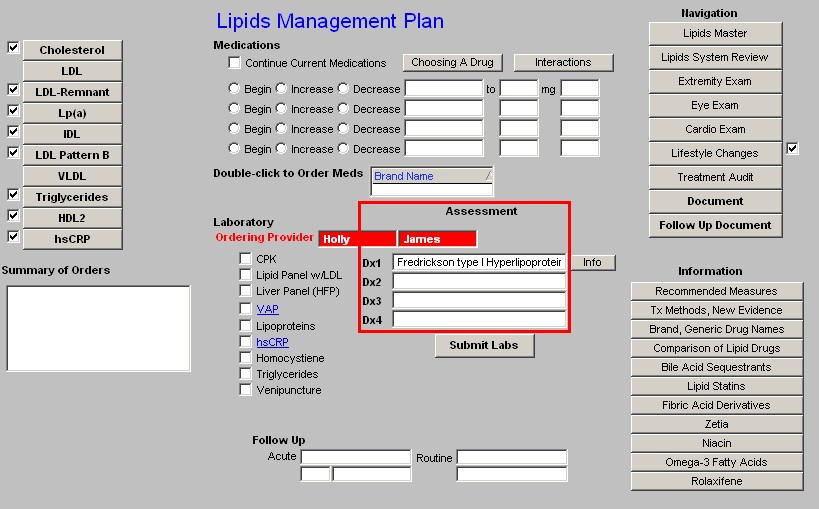
Note: When completed, the four Assessment options from the Lipid Plan will appear in the first four Assessment boxes on the Master GP Assessment Template. If you have already put data in those four boxes from another template, the Lipid Plan will overwrite them. Be aware of this and make allowance for it when using other templates for Assessment documentation.
Beneath the four Assessment boxes is a button entitled "Submit."
- Once you have completed the lab orders for Lipids
- Once you have completed the diagnosis for Lipids
- Click the "Submit" button and you will do four things:
- You will send the lab orders to the lab
- You will post the lab charges to the patient's chart
- You will place the lab orders on the Superbill - while this is not used any longer, it still exists and allows you to visually inspect your orders to see if you have done it correctly. You will find this function on the Master GP Plan Template.
- You will place the lab orders on the patient's chart.

Beneath the lab tests is an option to note the timing and reason for a follow-up visit.
Column 3 -
Navigation Buttons - the following navigation buttons appear at the top of this column
- Lipids Master
- Lipids System Review
- Extremity Exam
- Eye Exam
- Cardio Exam
- Lifestyle Changes
- Follow-up Document - this document should be generated and given to the patient at each visit for lipid management.
- Document - this is the chart note for the Lipid Management Suite of Templates. It should be generated each time these templates are used.
Information - these are provider education document on the following subjects:
- Recommended Measures
- Tx Methods, New Evidence
- Brand, Generic Drug Names
- Comparison of Lipid Drugs
- Bile Acid Sequestrants
- Lipid Stains
- Fibric Acid Derivatives
- Zetia
- Niacin
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
- Rolaxifene
|