|
Current format of The Chronic Care Management (CCM) Code was instituted by CMS in January 2015. It was first proposed in 2013 with a projection of beginning in 2014, but the requirements were such that it would have been virtually impossible for a primary care provider to successfully use it.
When the final version was released, changes had been made such that it could be used. Because the compliance requirements were specific and significant, SETMA decided not to deploy it until we had built a tool so that we could efficiently fulfill the billing demands and so that we could internally audit those requirements to prove that we were meeting all of the demands. The tool would also allow us easily to respond to a CMS audit if one were initiated.
SETMA’s deployment of Chronic Care Management can be found on the AAA Home template, as shown below outlined in green.
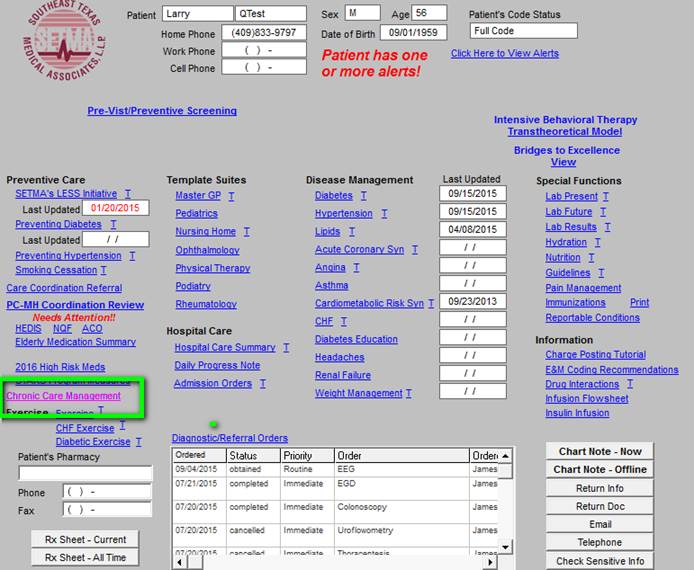
When the CCM button, outlined in green above, is deployed, the following Master CCM Template will appear. The master template is organized into five sections which will be explained individually.
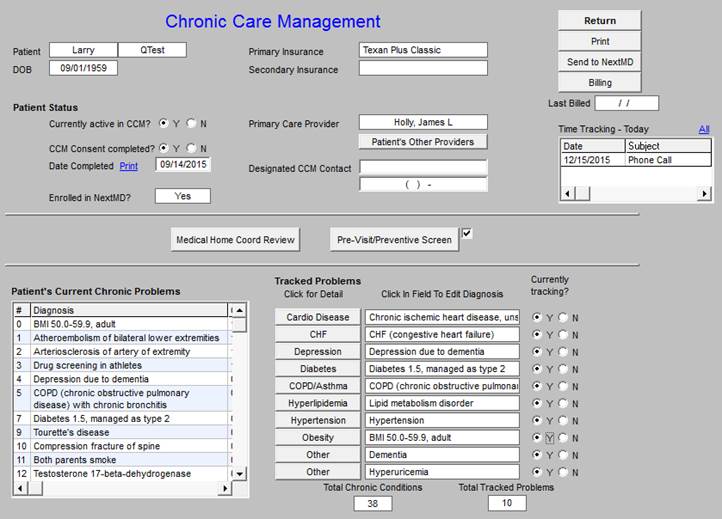
The first section shown below is organized into three columns with a bottom section containing two functions.
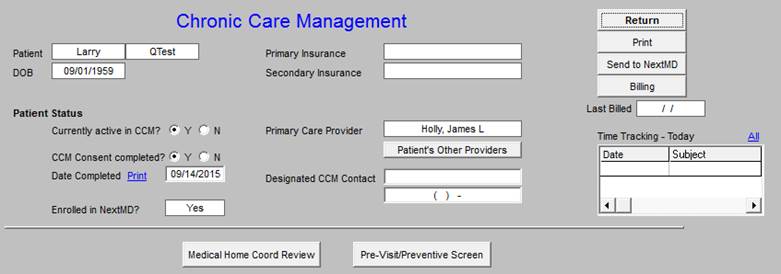
The first column includes the patient’s name and date of birth, which are automatically added to the template, followed by the Patient Status which includes the following information, which must be added by the provider:
- Currently active in CCM yes or no
- CCM Consent completed yes or no
- Date Consent completed
- Enrolled in NextMD? (this is SETMA’s web portal)
The second section displays the following functions:
- Primary Insurance (for the CCM this will be Medicare Fee-for-Service)
- Secondary Insurance (this is important because the patient will have a co-pay for CCM, which cannot be waived, while most of our patients cannot afford to pay the co-pay.
- Primary Care Provider
- Patient’s Other Providers - this button interacts with a similar function in the EMR
- Designated CCM Contact with telephone number
The Third Column includes the following:
- Return button which takes you back to the main EMR
- Print - this launches the printing of the current CCM document
- Send to NextMD - this sends the current summary document to the web portal from which the patient can access the document
- Billing - this launches the CCM Billing Requirement Check (Note: this automatically audits whether all required functions have been completed for the current contact to be billed)
- Last Billed - this alerts the provider to when the CCM was last billed.
- Time Tracing - Today - see explanation below
CCM Billing Requirement Check
Billing -- launched when the Billing button, seen above, is deployed. When all requirements are met, the notice seen below in green will appear which states: “You may bill a Chronic Care Management (CCM code for this patient. You may select the code below and when you click “OK’ the charge will be sent for billing.”
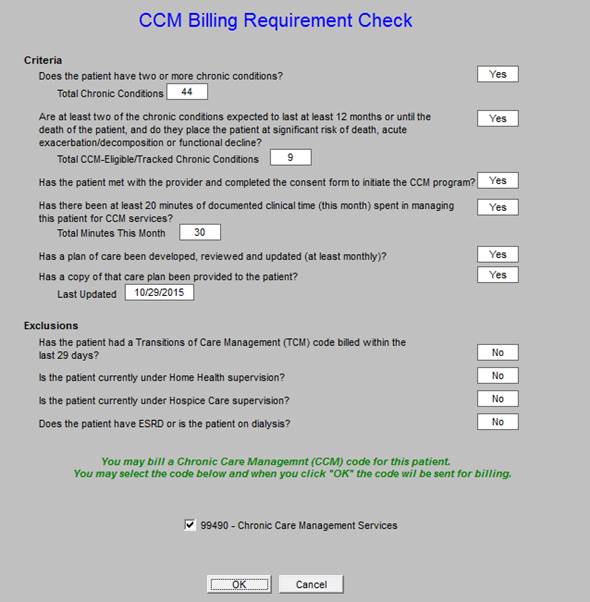
The template shows the requirements for CCM. The elements of this “Chronic Care Management Billing Requirement Check” are automatically and electronically audited. If the patient quantifies on the basis of all of the following, as per the above template, the provider will be alerted that a CCM Code can be billed. The provider can then click the box next to the 99490 CPT Code. Once the “OK” button has been clicked, the billing for the CCM Code will automatically be sent to SETMA’s Central Billing Office.
The participation and billing requirements for the CCM are:
- The patient must have two or more chronic conditions?
- Are at least two of the chronic conditions expected to last for at least one year?
- Do these chronic conditions place the patient and significant risk of exacerbation, decomposition or functional decline?
- Has the patient met with the provider & completed a consent to initiate CCM program?
- Has there been at least twenty minutes of documented clinical time spent this month spent in managing this patient for CCM services?
- Has a plan of care been developed, reviewed and updated at least monthly?
- Has a copy of that plan of care been provided to the patient?
- Has the patient been hospitalized in the past twelve months?
The following excludes a patient from participating in or receiving CCM services:
- Has the patient had a Transition of Care Management (TCM) code billed within the past 29 days?
- Is the patient currently under Home Health supervision?
- Is the patient currently under Hospice Care supervision?
- Does the patient have ESRD or is the patient on dialysis?
Time Tracking
The Time Tracking - Today function is seen below outlined in Green. Because the payment for CCM is dependent upon the completion of a 20-minute telephone contact and/or a total of 20-minute time spent on the patient’s care including a telephone contact each month, the ability to document and to audit the time spent is an important compliance issue.
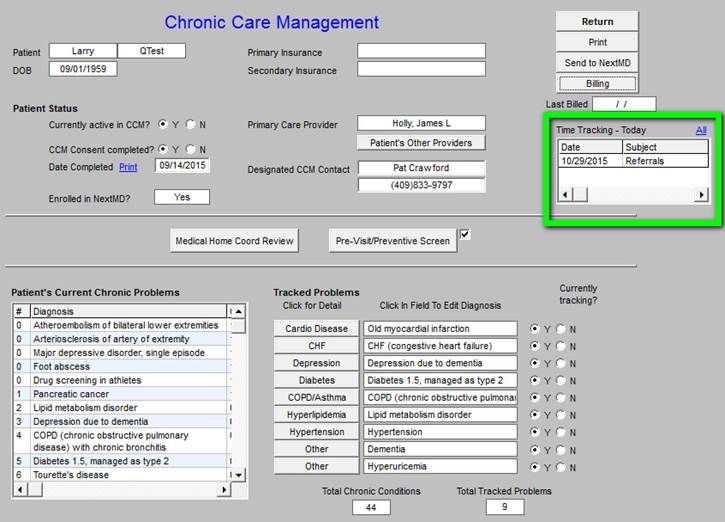
This is how the time tracker functions
The provider includes their name, date, start time and stop time of the activity being documented. The provider then documents the type of activity as seen in the “subject” below and then adds a descriptive note as to what was done for and with the patient. The “total” time is then automatically calculated. When this function is accessed multiple times during one month, such as completing referrals, or other care coordination functions, and a telephone call, the cumulative time will be noted on the last episode, once again allowing demonstration of compliance with the requirements for billing with this code.
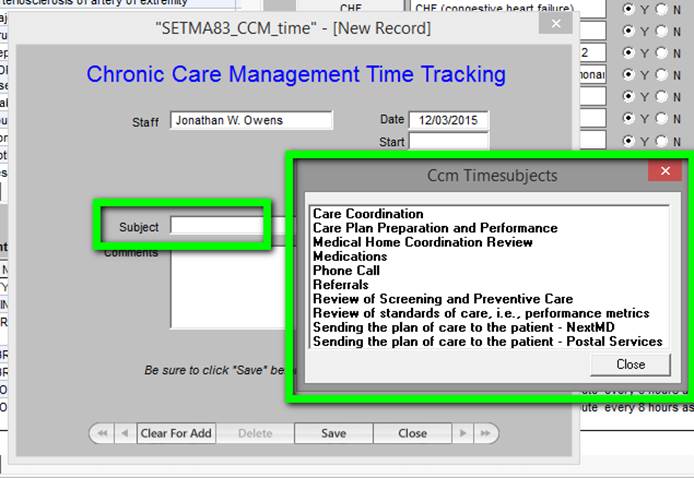
Outlined in green below are the options in a drop down menu for documenting the tasks which were performed in the current CCM call. Others will be added as we have more experience with this function.
When the “All” button on the time tracker is deployed - see below outlined in green - a summary of the time spent in the CCM Code functions is calculated. This will allow SETMA’s provider to audit their own performance to make sure that we are remaining in compliance with CMS requirements.
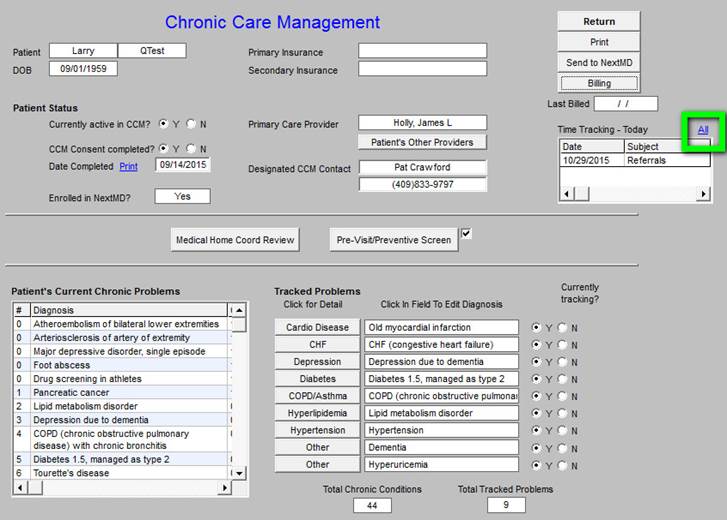
When the “All” button, seen above outlined in green, is clicked, the following summary of “time spent” will be displayed.
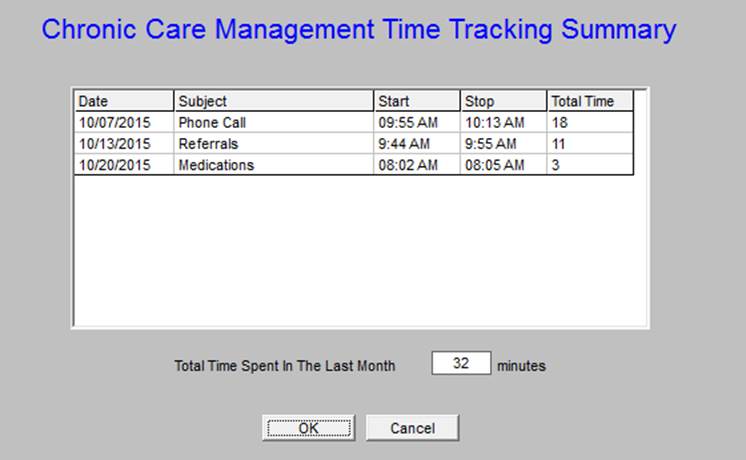
At least 20 minutes must be documented each month in order to support the charge for the CCM Code.
The last functions of the first section, which is seen below are the Medical Home Coordination Review and the Pre-Visit/Preventive Screen. They are outlined in green below.
Medical Home Coordination Review
The details of this template are explained in pages 4 - 26 at the following link:
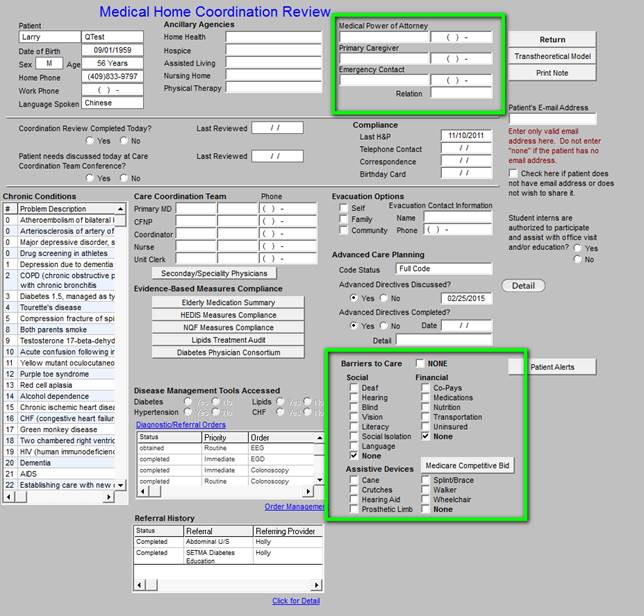
http://jameslhollymd.com/EPM-Tools/pdfs/tutorial-medical-home-coordination-review-tutorial.pdf. In relationship to the CCM Code, this template is deployed by clicking on the button seen above. In relationship to the CCM, it is important to assess: Barriers to Care and Screening and Preventive Care. This can be done as is described in the following two screens.
The Barriers to care can be documented with the following details: social, financial, assistive devices should be completed. In addition the following should be completed: the Medical Power of Attorney, Primary Care Giver, and Emergency Contact.
Screening and Prevention
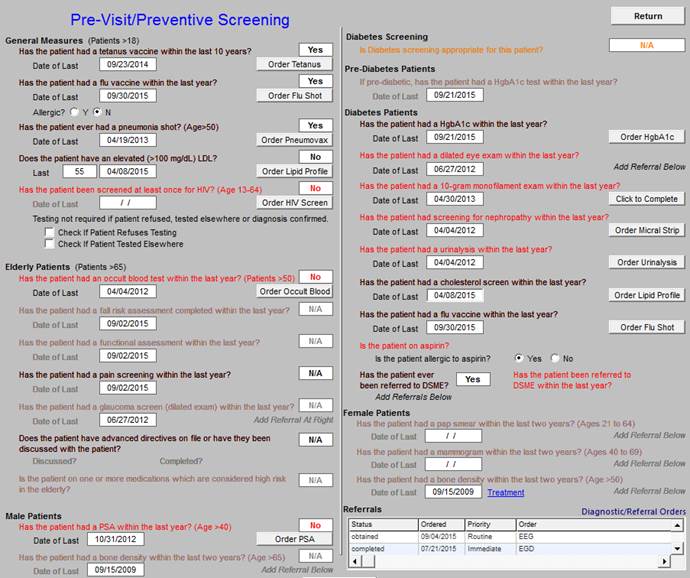
To fulfill the CCM Code function, it is also necessary to evaluate the patient’s screening and prevention care. This can easily be done by clicking the button entitled Pre-visit Screening and Preventive Care. This screen alerts you to assess the healthcare needs which are as yet unmet in the patient’s care. During the CCM call, this should be reviewed and if the patient has unmet needs, they should be given an appointment or a referral made for the function to be completed.
When this button is deployed, the following screen appears which automatically alerts the provider to any unfulfilled screening or preventive health needs in the patients care. All elements in red apply to the patient and have not been done; all elements in black apply to the patient and have been done and all elements in grey, do not apply to the patient.
The second section of the Master CCM template is shown below. It has four columns and like the first section, two additional functions are displayed across the bottom of this section.
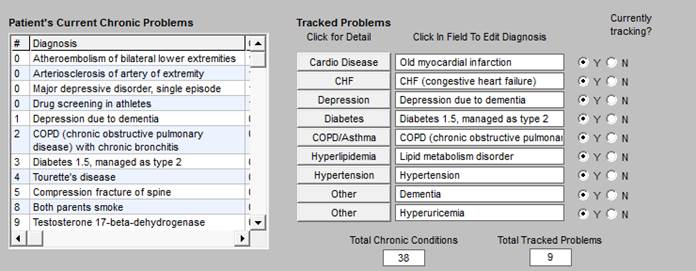
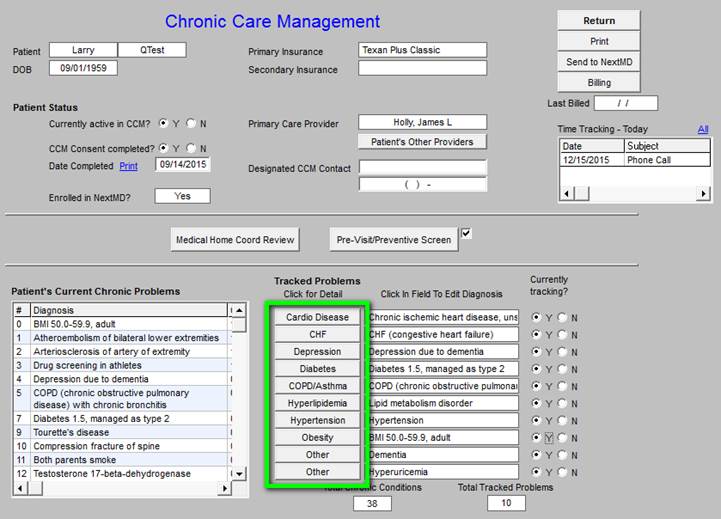
- Because the CCM interacts with the full EMR, the Patient’s Current Chronic Problem list is automatically display in the first column.
- The second column has a list of Tracked Problems. When you click on any of the problems, the details of the tracking will display. There are eight problems (obesity has been added) which are structured with two other options for problems unique to a particular patient.
- The third column is entitled Click in Field To Edit Diagnosis. This will allow the provider to select the specific diagnoses from the patient’s Current Chronic Problem List.
- The fourth column entitled Currently Tracking? allows the provider to denote whether or not a particular diagnosis is currently being tracked. If it is not, this will be left blank.
At the bottom of this section of the Master CCM Template are two boxes which display two numbers which enable SETMA to audit for compliance with the requirements of the CCM.
- Total Chronic Conditions - this automatically displays the number of active diagnoses in the patient’s care which meet the criteria for inclusion in the CCM.
- Total Track Problems - this displays the number of conditions being tracked for this patient.
This allows for efficient auditing of the use of the CCM to make sure we remain compliant.
The third section of the Master CCM Template displays the patient’s current, active medication list. The medication list can be reconciled during the call. If the Reconcile button outlined in green below is activated, a template appears which allows a medication reconciliation to be completed and documented.
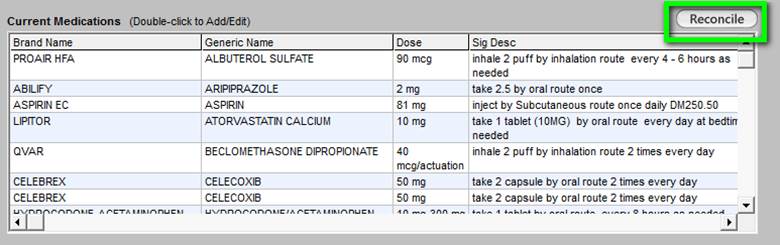
At the top right, there is a button entitled Reconcile. When activated, this button launches the following template through which a formal medication reconciliation can be done. Below is what is launched when the button is clicked.
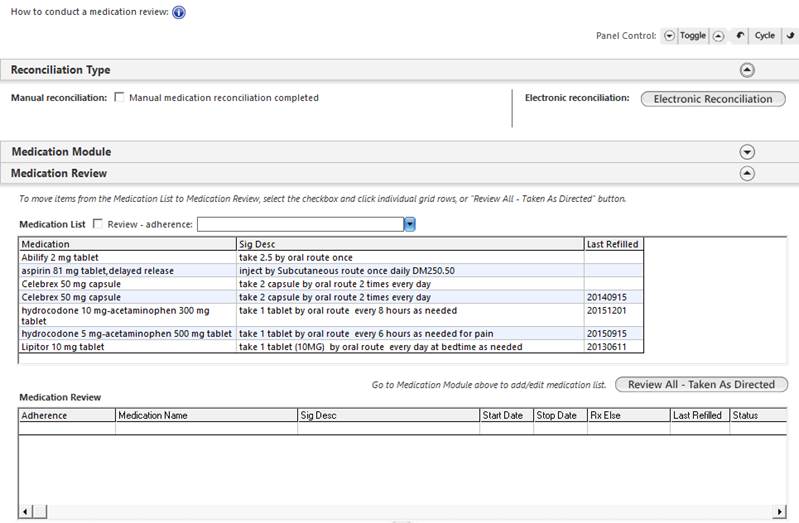
The use of this template is explain elsewhere and will not be repeated here.
The fourth section of the Master CCM Template displays:
- Current Allergies - left handed window
- Referrals - this shows the referrals that are currently outstanding with their status, priorities, content and ordering provider.
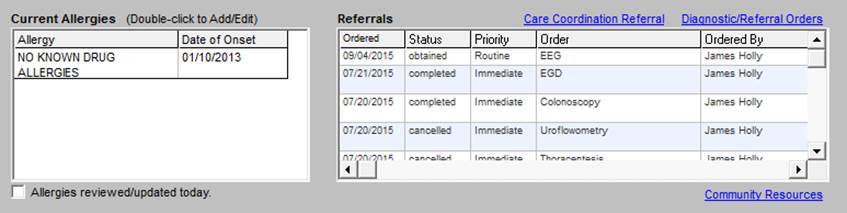
At the top right of this section of the template there are two functions which are hyperlinks in blue:
- Care Coordination Referral
- Diagnostic/Referral Orders
Across the bottom of this section there are two other functions:
- Allergies reviewed/updated today -- A check box for documenting that the allergies were reviewed on this day’s telephone call.
- Community Resources - a list of agencies which can provide services needed by patients.
These four functions are described below.
Care Coordination Referral
It is with this template that patients are referred for additional care and/or for financial asisstance from the SETMA foundation. All referrals are managed by SETMA Care Coordination Depatement. The options are directed by the template.
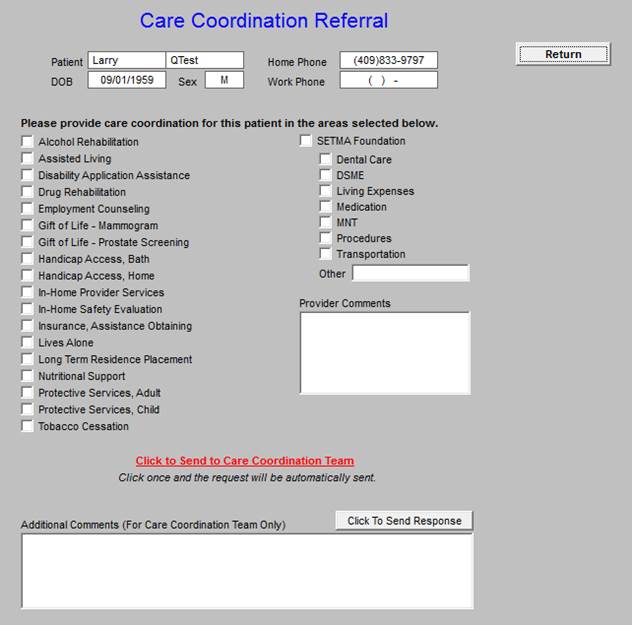
Once the needed services are noted by clicking in the box next to the functions in the first and second collumn and once any comments are placed in either of the comment boxes seen above, the button in red entitlled “Click to Send to Care Coordination Team” is deployed. The refferal is then sent to Care Coordination and the button’s color is changed to green.
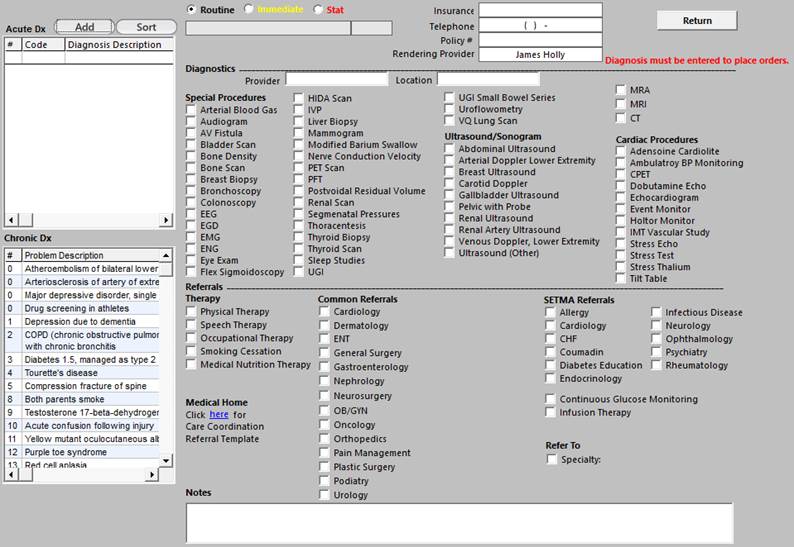
Diagnostic/Referral Orders
This is SETMA’s Refferal tempaltetemplate. It works with SETMA’s referral depatemnt and is deployed from this template and/or from our EMR.
This is a list of Community Resources which are available to our patients.

The fifth section of the CCM Master Template displays:
- Appointment History (3 Months)
- Upcoming Appointments (3 months)
Structured Data for Following the Chronic Care Conditions
Structured data fields are provided for 8 conditions which are outlined in the green box below. These represent the most common Chronic Conditions examined in CCM. Other diagnoses can be added in the “other” fields. To the left of that box, there is a list of the patient’s Chronic Conditions. This allows the provider making the telephone call to ask about other conditions.
The following are structured-data fields for the monitoring of needs and statuses of each of these conditions.
Chronic Care Management for Cardiac Disease
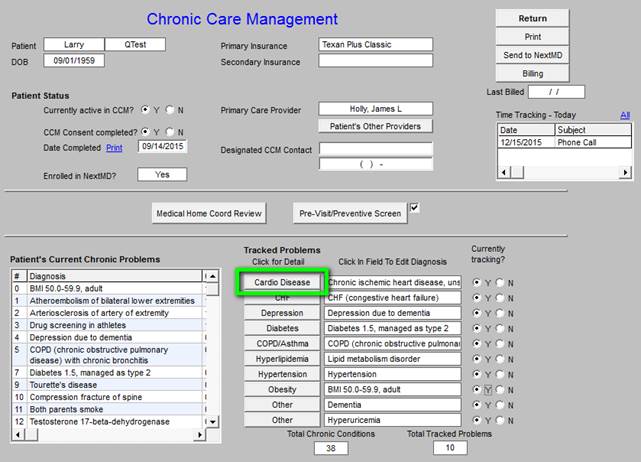
Below is the template which is deployed by clicking on Cardio Disease.
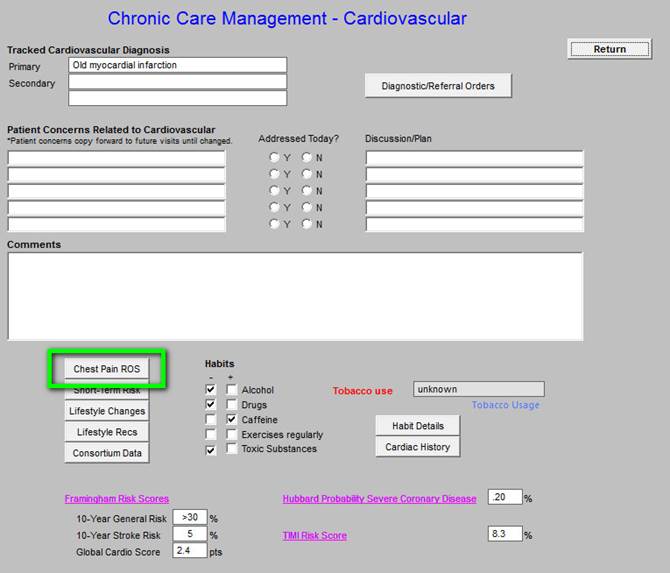
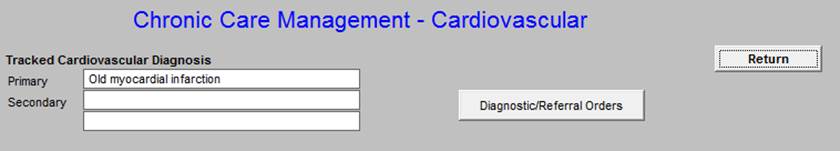
The Top section includes:
- Tracked Cardiovascular Diagnoses - selected from the patient’s Chronic Problem list
- Diagnostic/Referral Orders - master referral template assessable from here
Middle section
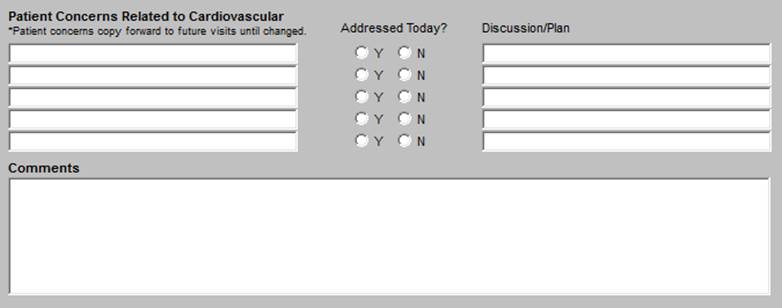
- Patient’s Concerns Related to Cardiovascular
- Addressed Today - check boxes to note whether a condition was addressed or not.
- Discussion/Plan
- Comment box for free text additions
Third section
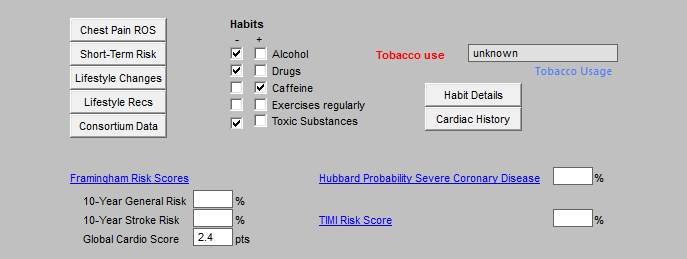
The first column in the third section includes (the details for each are presented below):
- Chest Pain ROS -- Angina Review of Systems
- Short Term Risk
- Life Style Changes
- Life Style Recommendations
- Consortium Data
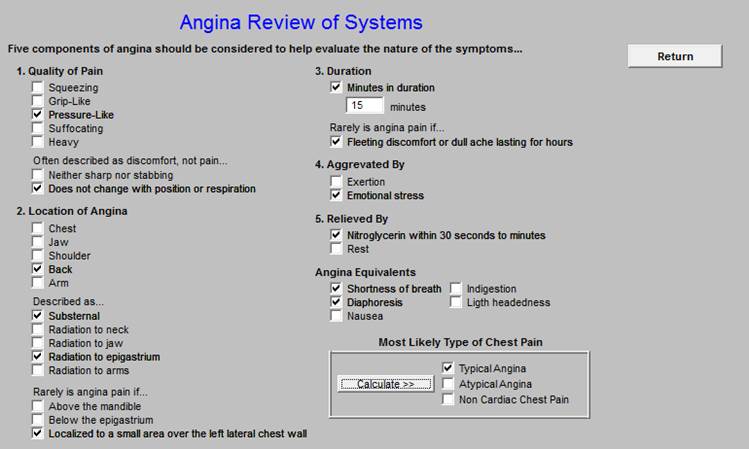
Chest Pain Review of Systems - Angina Review of Systems
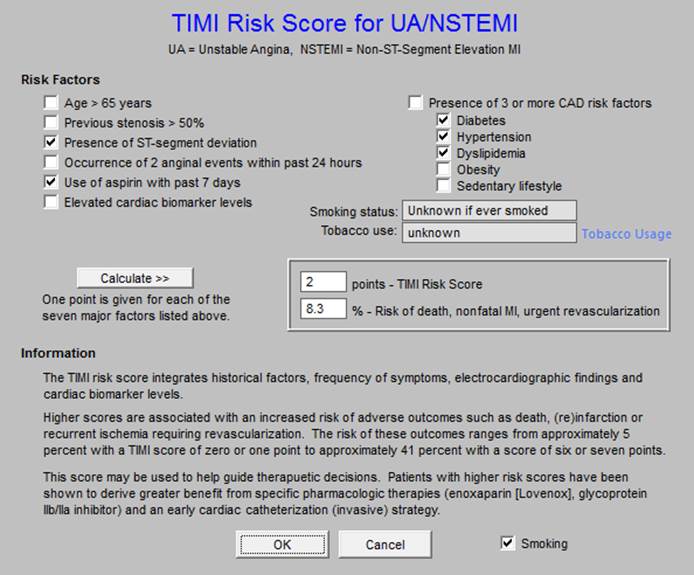
Short-Term Risk of Death or Non Fatal MI in Patients with Unstable Angina

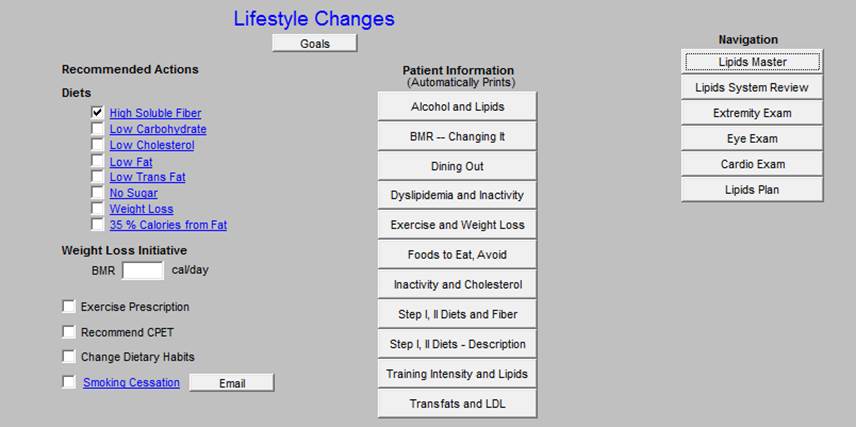
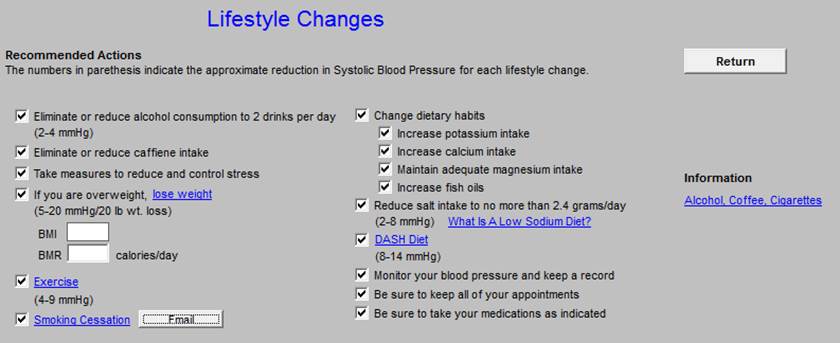
Life Style Changes
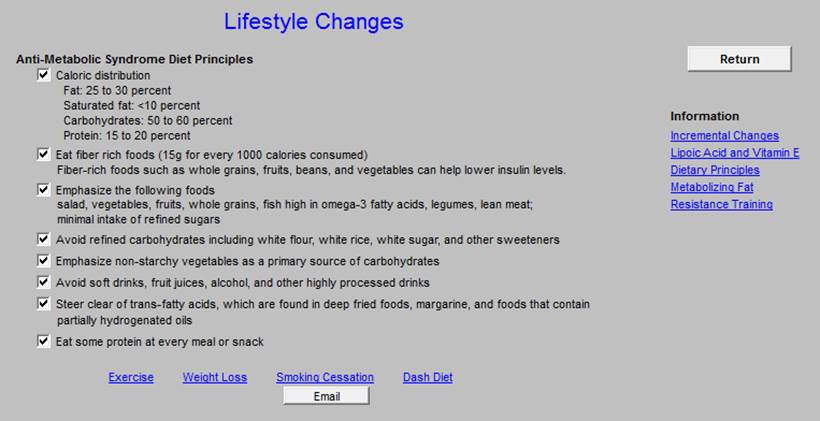
Lifestyle Recommendations for cardiovascular risk factors.
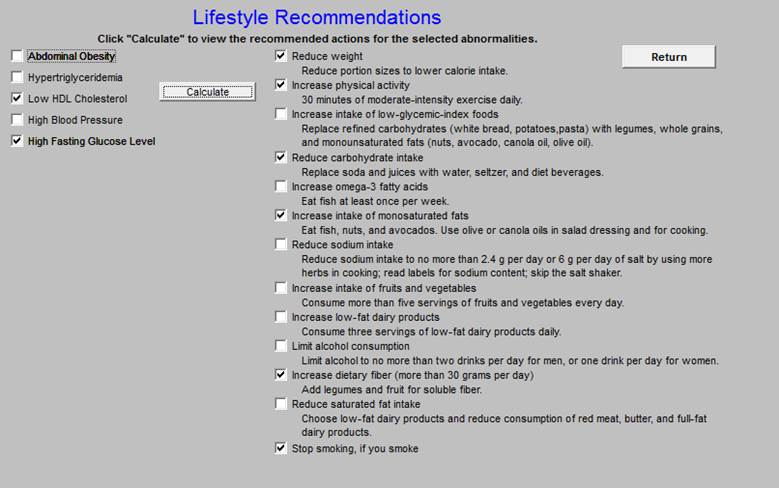
Physician Consortium for Performance Improvement (PCPI) Data Set
The second column in the third section includes Habits:
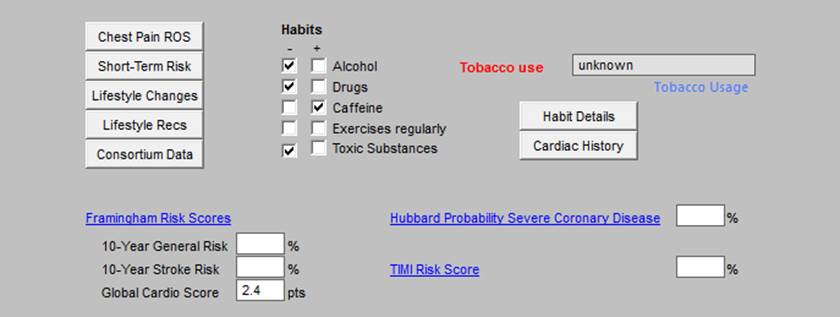
- Alcohol
- Drugs
- Caffeine
- Exercise Regularly
- Toxic Substances
These are all populated automatically from documents in the man EMR data base.
The third column in the third section includes:
- Tobacco Use
- Habit Details
- Cardiac History
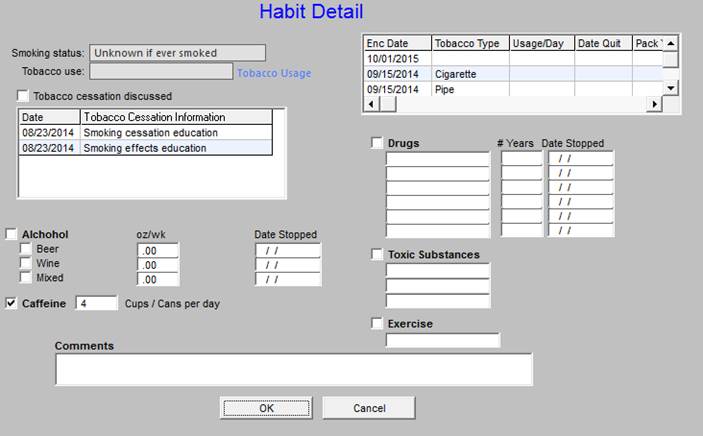
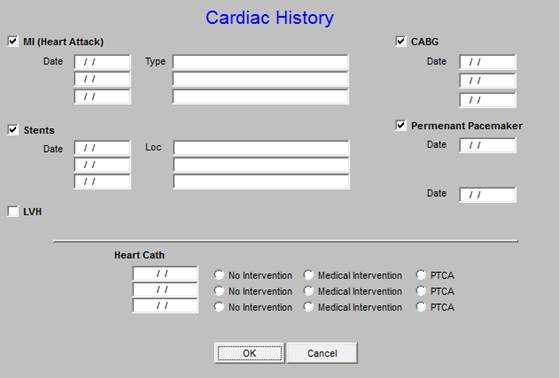
The fourth section includes hyperlinks to three functions related to cardiovascular disease (the details for each are presented below):
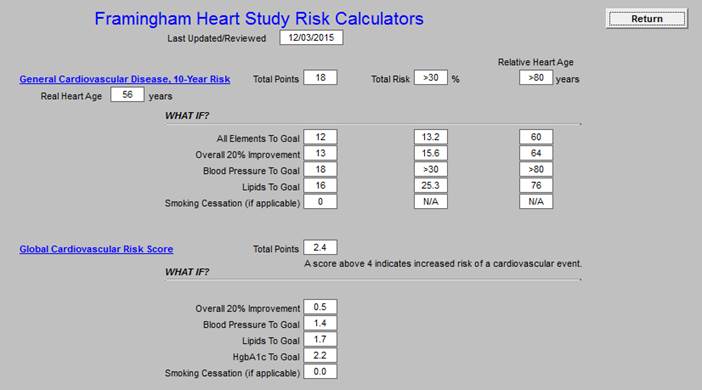
- Framingham Risk Score
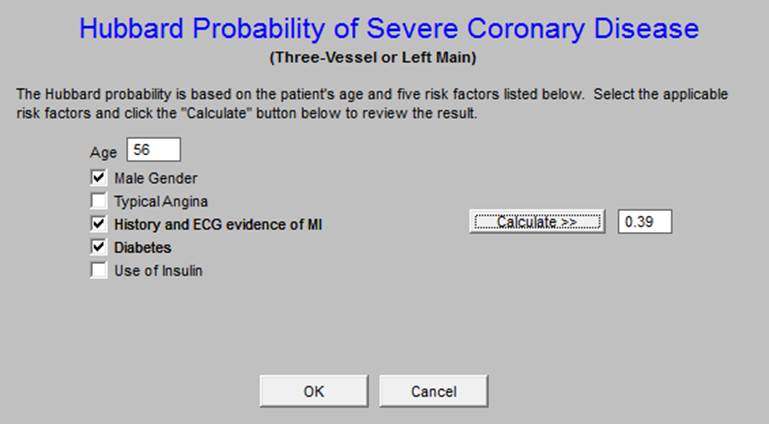
- Hubbard Probability Severe Coronary Disease
- TIMI Risk Score
Framingham Heart Study Risk Calculators
Hubbard Probability of Severe Coronary Disease
TIMI Risk Score for Unstable Angina and Non-ST Elevated MI
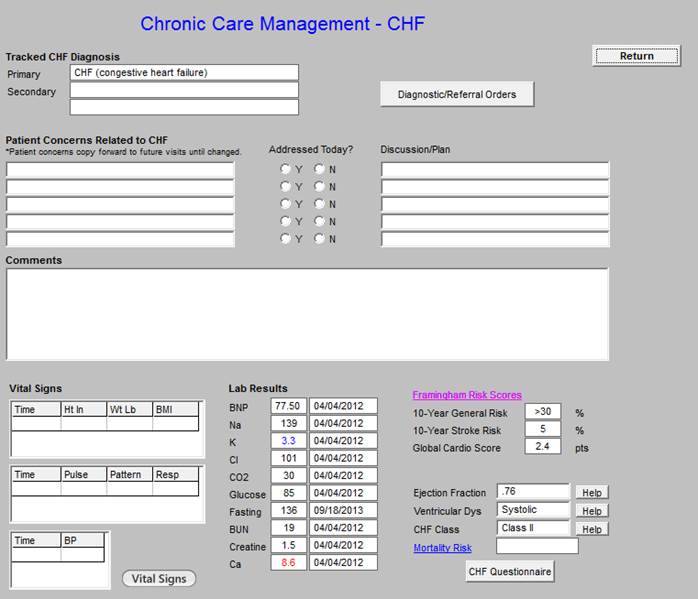
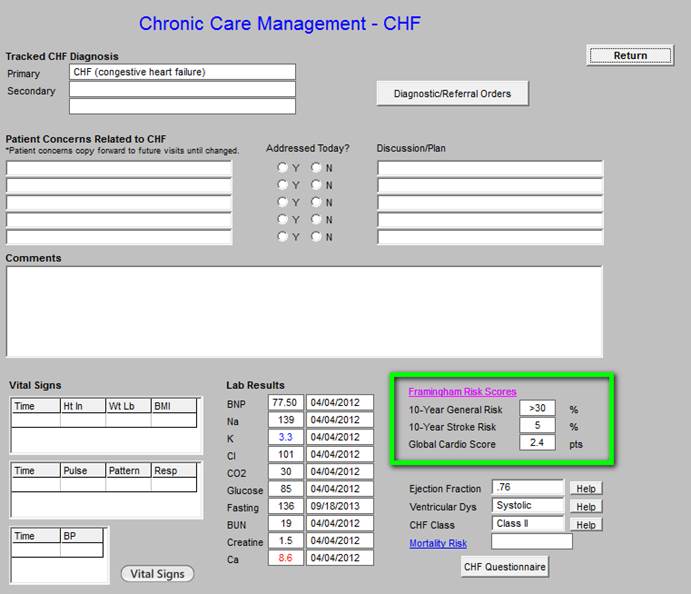
Chronic Care Management - Congestive Heart Failure
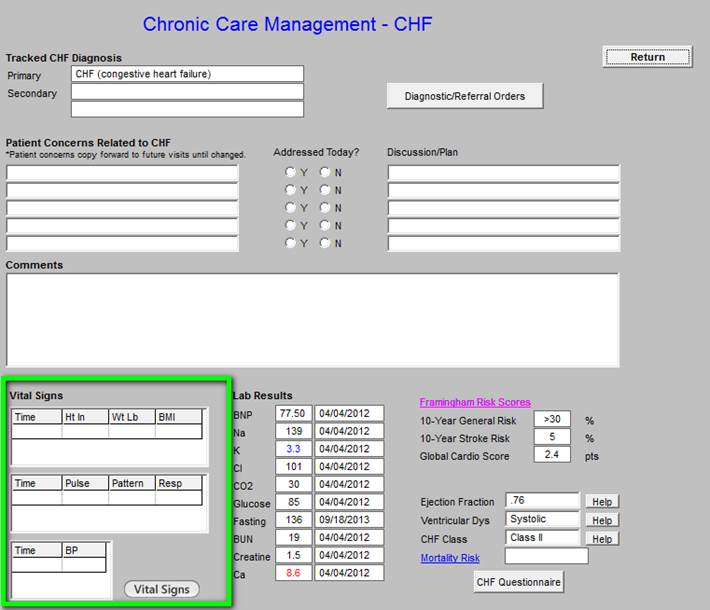
The vital signs outlined in green contain information pulled from the most recent visit.
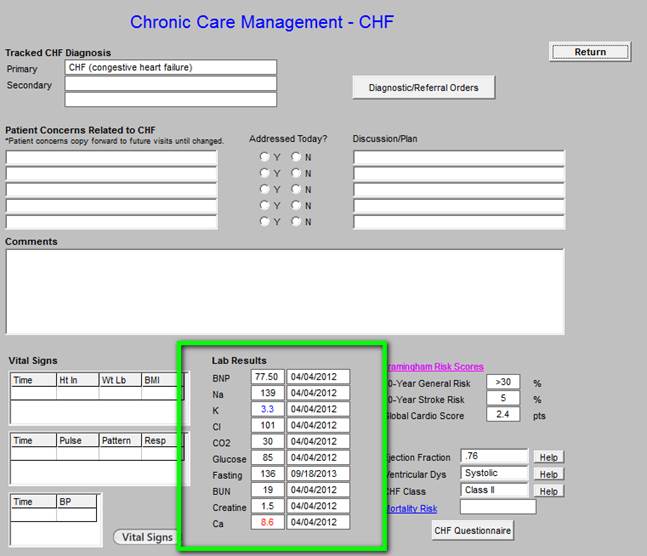
The laboratory values outlined in green above are automatically pulled from the most recent data.
The data outlined in green below is from the Framingham Risk Scores and is pulled from the main EMR data base.
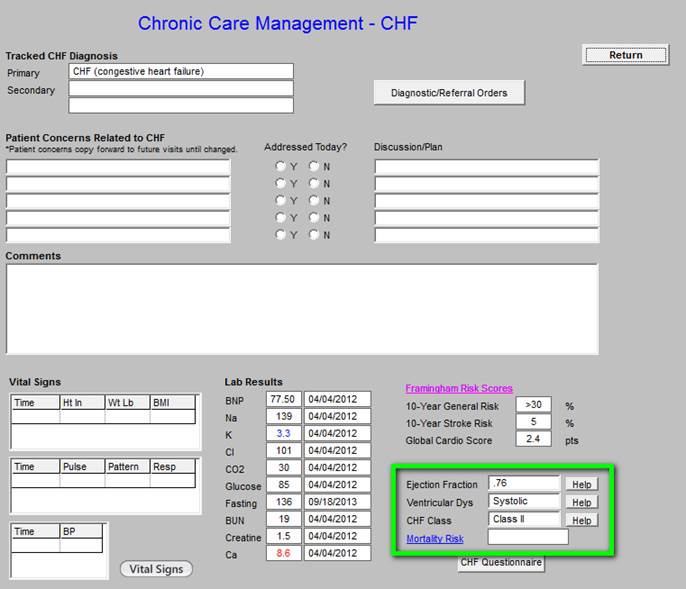
The information outlined in green above is pulled automatically from the main EMR; if it is not present, the echocardiogram should be ordered or documented in the EMR.
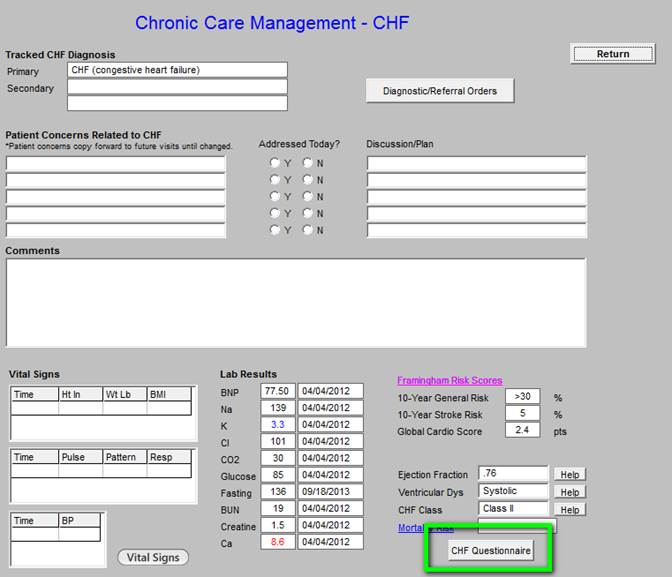
The CHF Questionnaire outlined below in green can be deployed by clicking on the button. In the course of CCM for CHF, this questionnaire should be completed annually.
Chronic Care Management -- Depression
This is the master template for Chronic Care Management - Depression. Like all of the Chronic Care Management, structured data templates there are the following in the Master Template below:
- Tracked Depression Diagnosis, selected from the patient’s Chronic Problem list.
- Diagnostic/Referral Orders - this allows the healthcare provider to complete referrals while making the monthly telephone call.
- Document the Patient Concern Related to Depression
- Document the Discussion/Plan
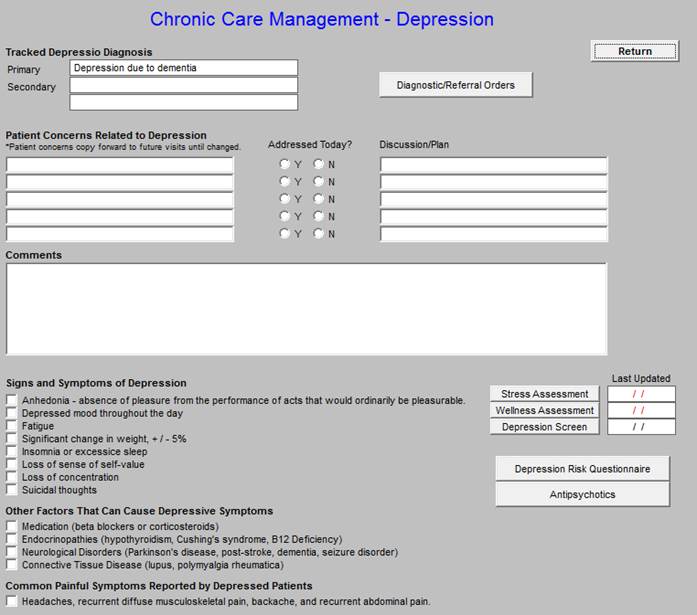
Signs and Symptoms of Depression - seen below outlined in green. The caller can easy document the symptoms of depression being experienced by the patient. The following link is to SETMA’s Depression Tutorial: http://jameslhollymd.com/epm-tools/Tutorial-Depression. This explains the below tools in more detail.
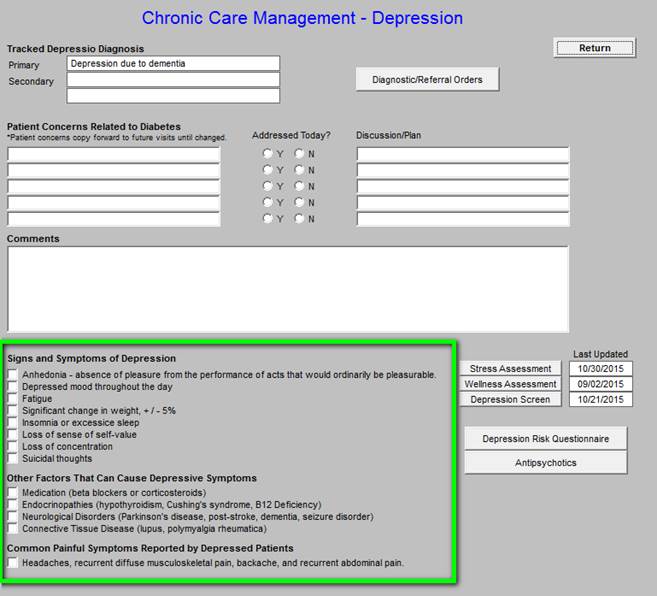
In the right-hand column the following tools are accessible and each is explained below; they include the following. To the right of the first three are the dates of last completion of these screening tools.
- Stress Assessment
- Wellness Assessment
- Depression Screen
- Depression Risk Questionnaire
- Antipsychotic Medication Tool
The above five tools are displayed in the following screen shots:
Stress Assessment
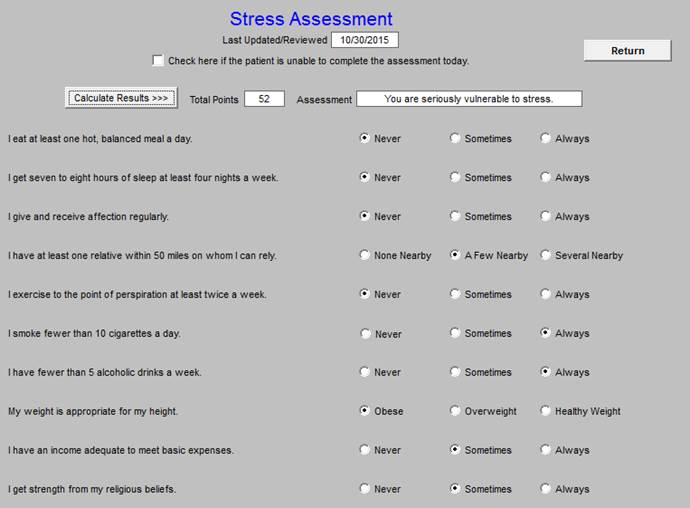
Wellness Assessment
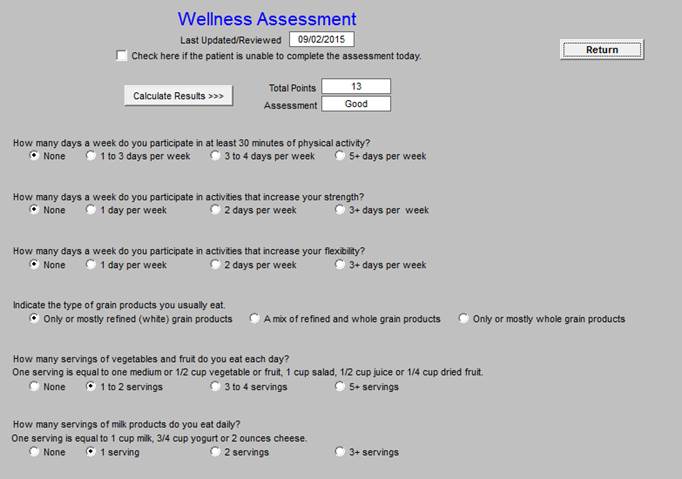
Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology (QIDS)
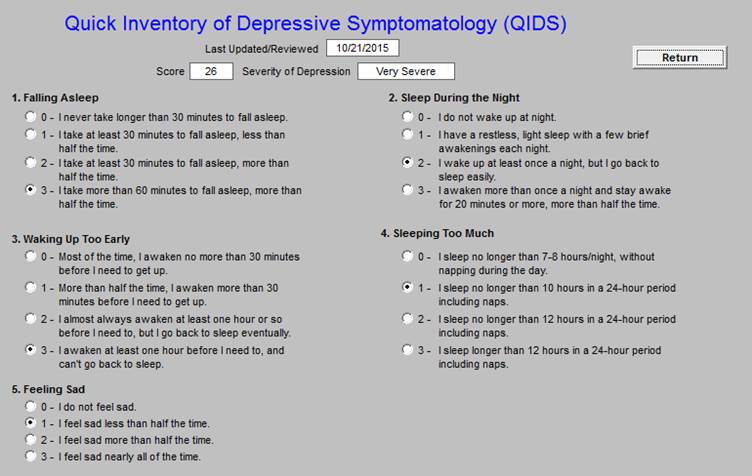
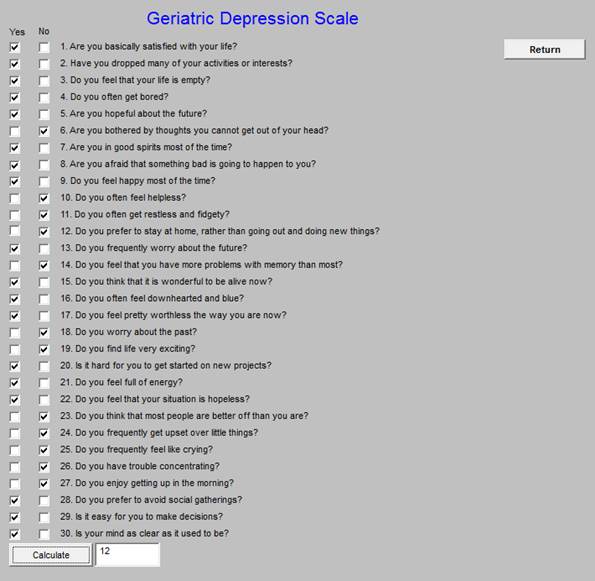
Geriatric Depression Scale
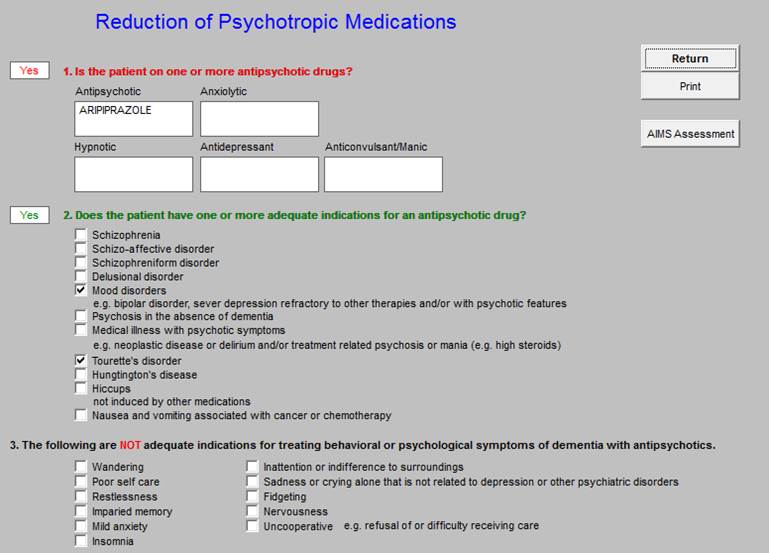
Tool for Reducing the Use of Antipsychotic Drugs
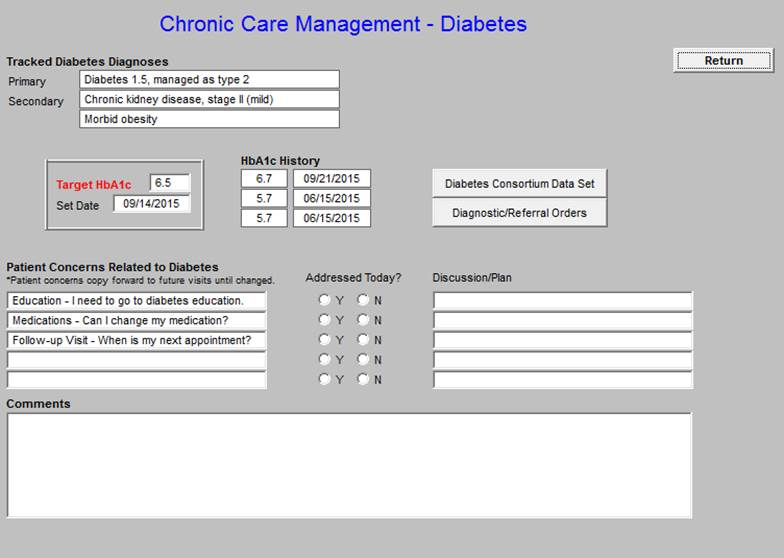
Chronic Care Management - Diabetes
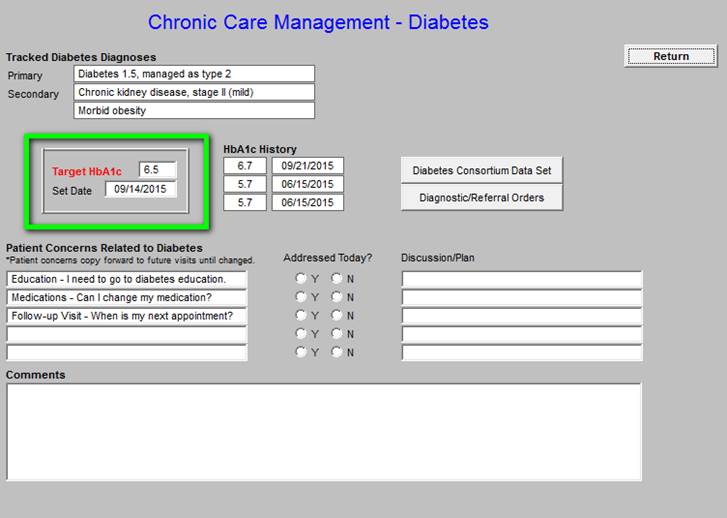
The last three HbA1c values are displayed with the Target A1c and the date the goal was set.
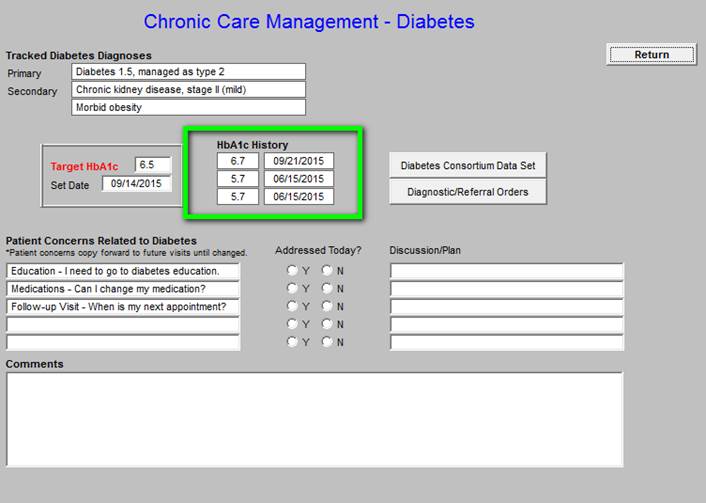
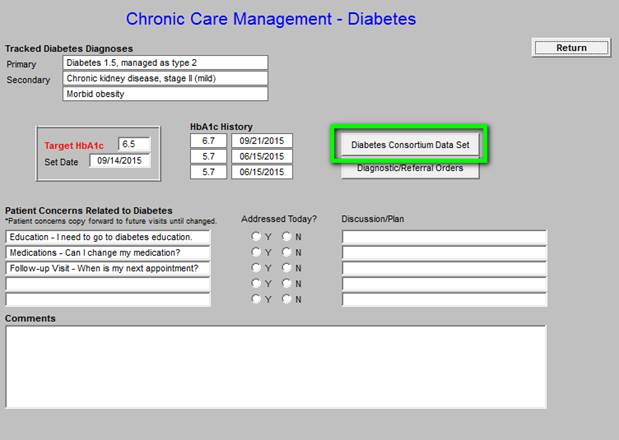
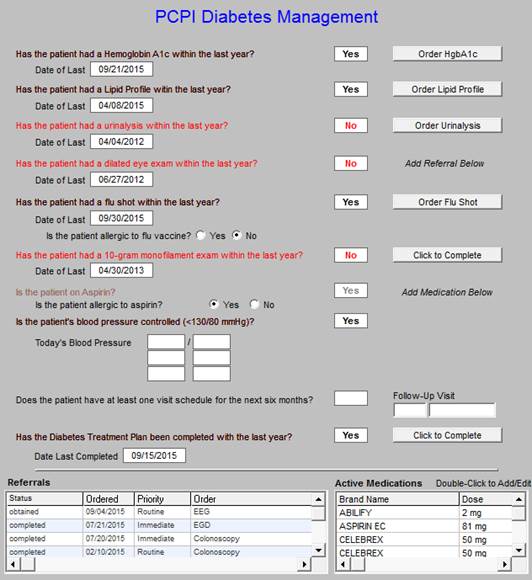
Quality Metric sets and standards of care for diabetes is deployed by clicking on the button outlined in green above. When that button is deployed, the following PCPI Diabetes Management measurement set is displayed. The legend is the same as in all SETMA disease management quality measurement tools: elements in black apply to the patient and have been done; elements in read apply to the patient and have not been done. If an element has not been completed, the provider can click the button in the right hand column and the function will be done. (Note: Because this interview will be done on the telephone, if an element is ordered the interviewer will have to be sure that the patient schedules an appointment or knows to come to the lab to have the testing done.)
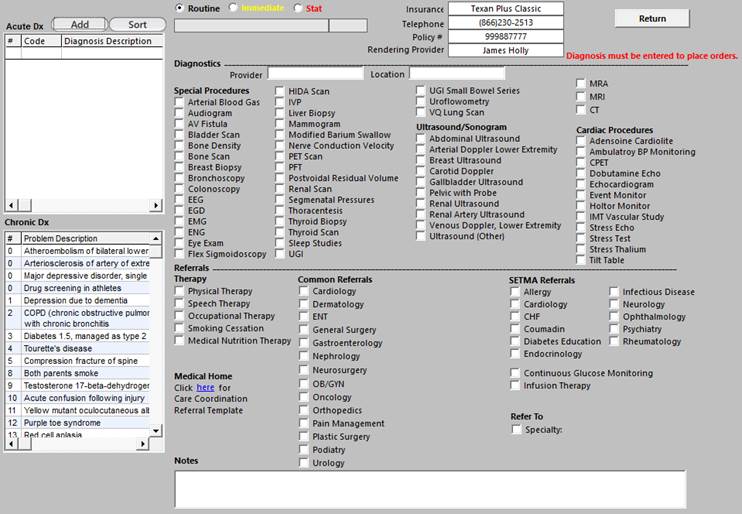
If this review indicates that testing should be done, it can be done by clicking on the Diagnostic/Referral orders button outline in green below.
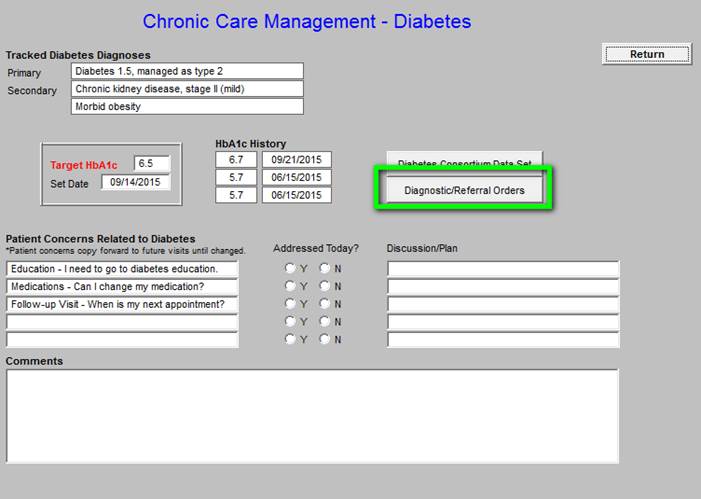
The following is the referral template.
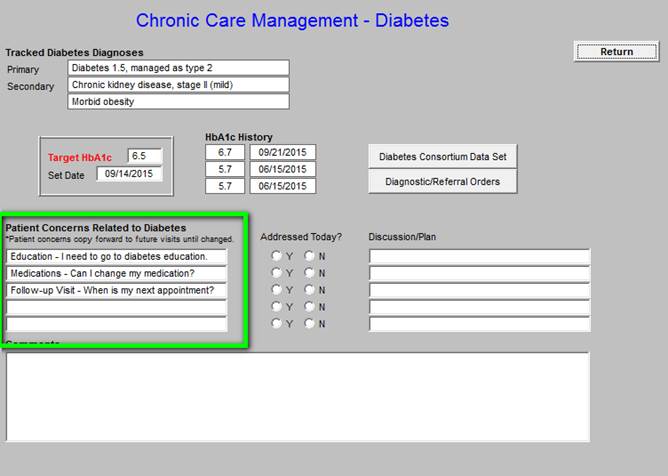
Below, outlined in green allows documentation f the Patient Concerns Related to Diabetes.
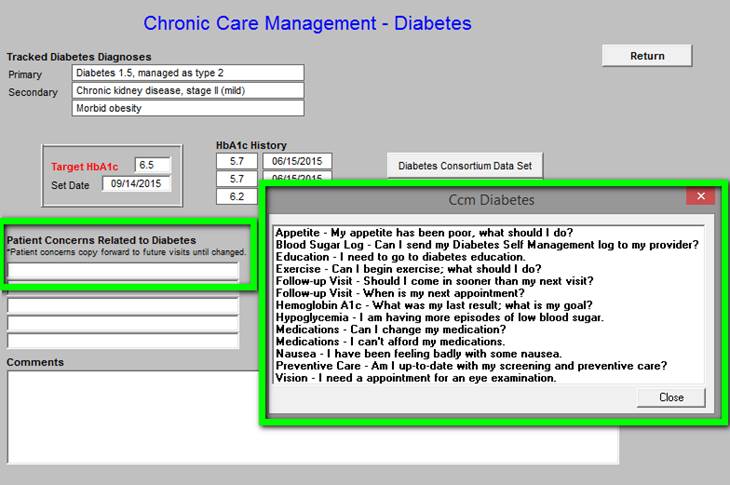
Patient Concerns Related to Diabetes -
As can be seen, the patient’s diagnoses related to diabetes are automatically displayed. Also the patients current and last three Hemoglobin A1Cs are automatically displayed. The patient’s target HbA1c is “set” and the date of that target being set is displayed. As can be seen just above the material outlined in green, there is a button entitled the Diabetes Consortium Data Set. This is the eight element data set published by the Physician Consortium for Performance Improvement. SETMA tracks this data, along with data audits for six other comprehensive data sets for diabetes. By provider name the results of these audits is published at www.jameslhollymd.com under Public Reporting. Data from 2009 to date is published.
In the first column on this template is a tool for document Patient Concerns Related to Diabetes. A note indicates that these concerns “copy forward” to subsequent Chronic Care management calls. The larger box in the second column which is also outlined in green gives a set of options which can be easily added to the Patient Concerns list.
Chronic Care Management - Asthma/COPD
The following is the Master Template for the Chronic Care Management - Asthma COPD. The Tracked Asthma/COPD Diagnoses, Diagnostic/Referral Orders, Patient Concerns Related to Asthma/COPD, Discussion/Plan and Comments box are similar to all of the structure fields.
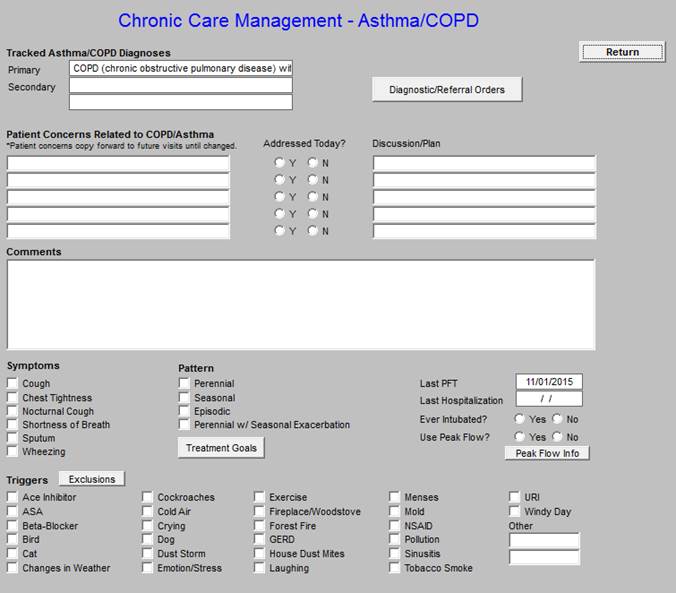
The following allows for the efficient documentation of the goals of asthma and/or COPD treatment

If the patient has not had a PFT in the past two years (see documentation in the boxes outlined in green), one should be ordered.
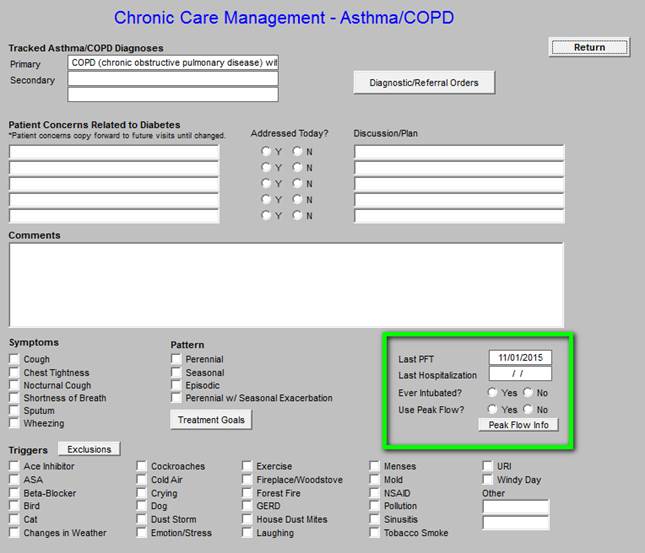
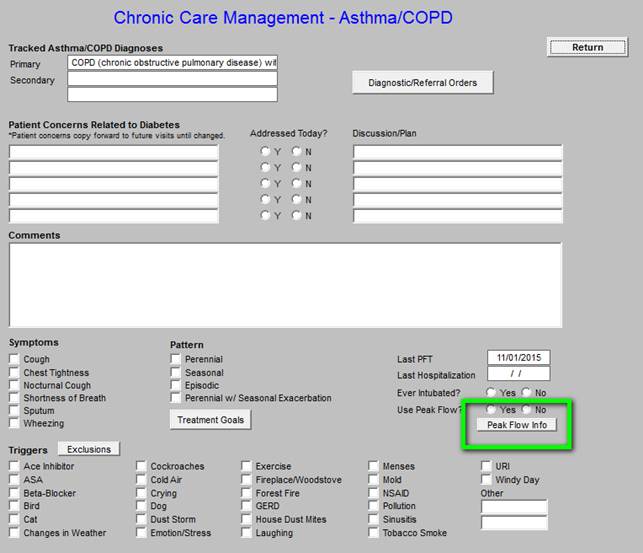
The patient should be taught how to obtain and interpret the Peak Flow Meter.

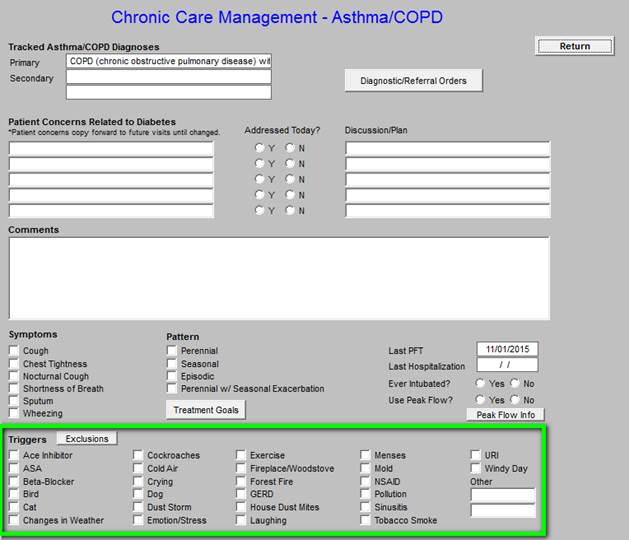
Outlined below in green are “triggers” for asthma and COPD exacerbation. During the course of the year, these should be addressed.
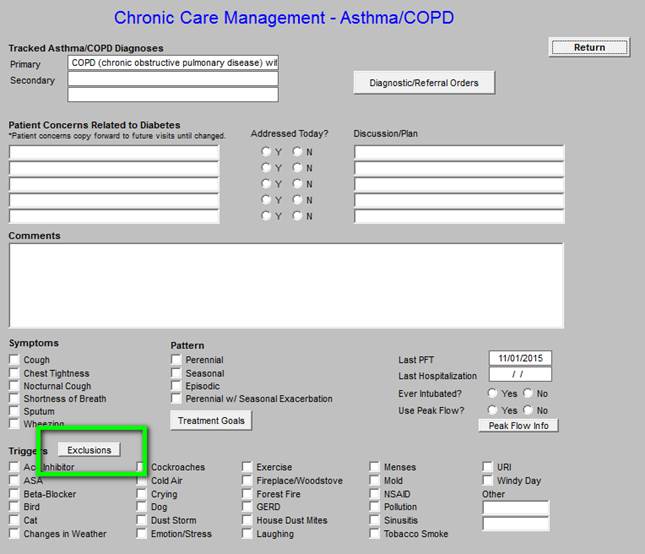
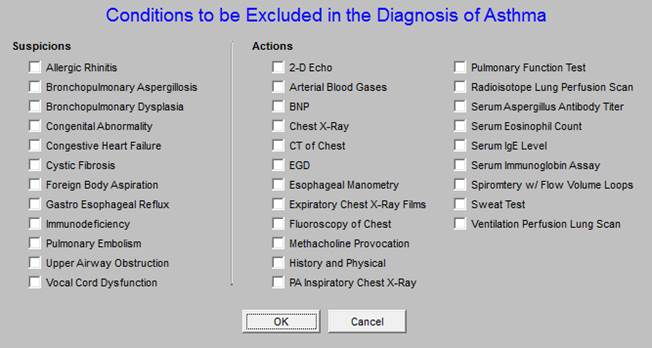
When the button outlined below in green entitled “Exclusions” is clicked, the following template is deployed. The “exclusions” are diagnoses which should be excluded in the diagnosis of asthma.
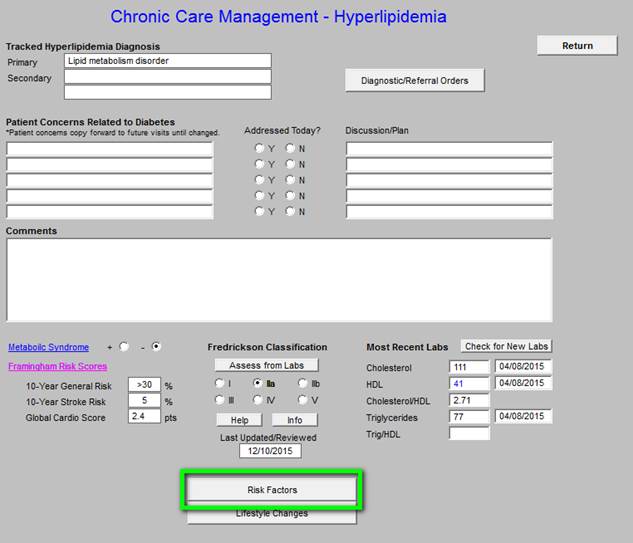
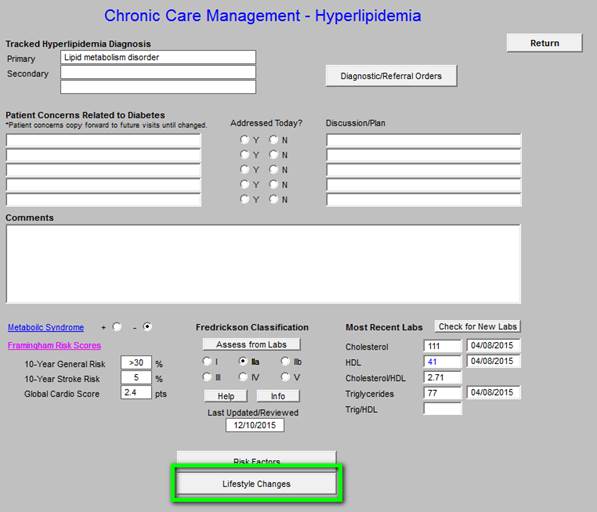
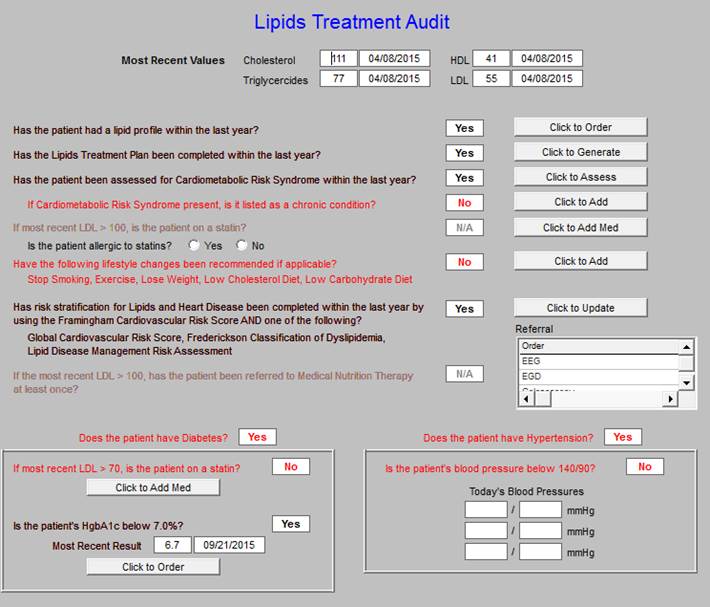
Chronic Care Management -- Hyperlipidemia
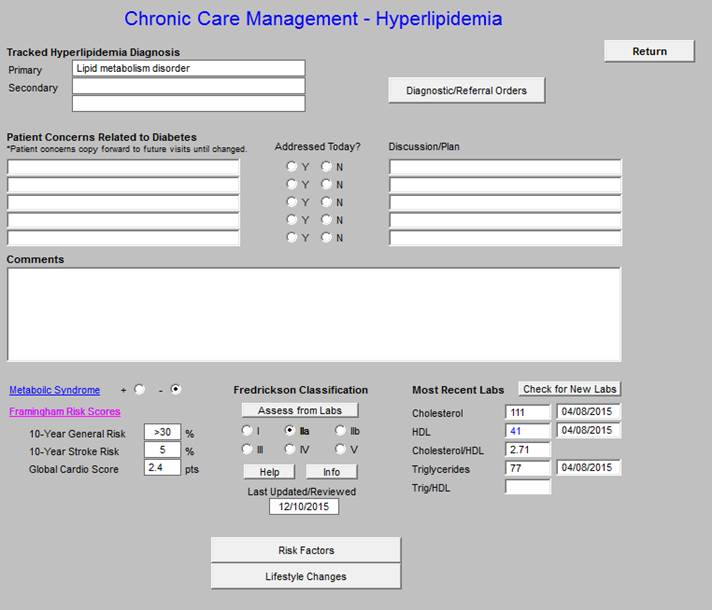
The following functions are available on this Chronic Care Management tool:
- Metabolic Syndrome calculator and the designation of whether or not the patient has the Cardiometabolic Risk Syndrome.
- Framingham Risk Scores
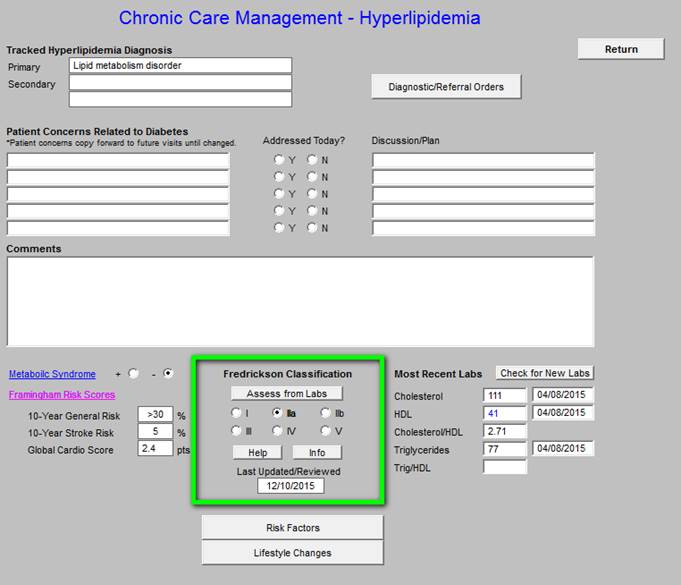
- Fredrickson Classification for Dyslipidemia
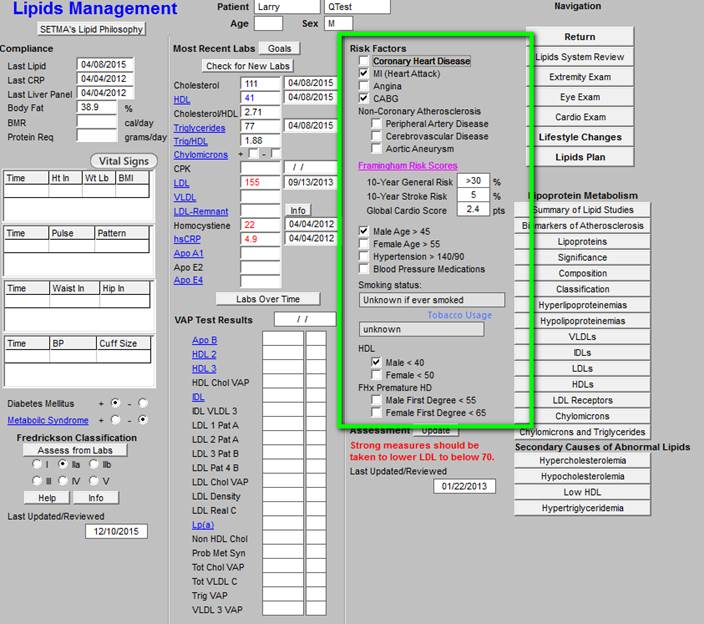
- Risk Factors for hyperlipidemia
- Lifestyle changes for treating Dyslipidemia
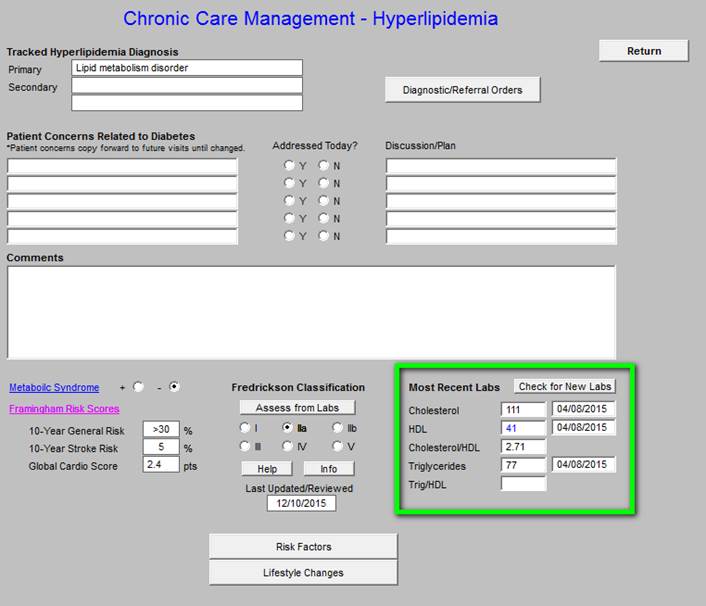
- In the right hand column, the follow values appear:
- Most Recent Labs - depress button to display most recent labs.
- Cholesterol
- HDL
- Cholesterol/HDL Ratio - optimally, this ratio should be below “4.”
- Triglycerides
- Trig/HDL Ratio - optimally, this ratio should be below “2,” a higher value indicates insulin resistance.
The aggressiveness of treatment of lipids is dictated by risk factors such as Framingham, Metabolic Syndrome, level of HDL and LDL.
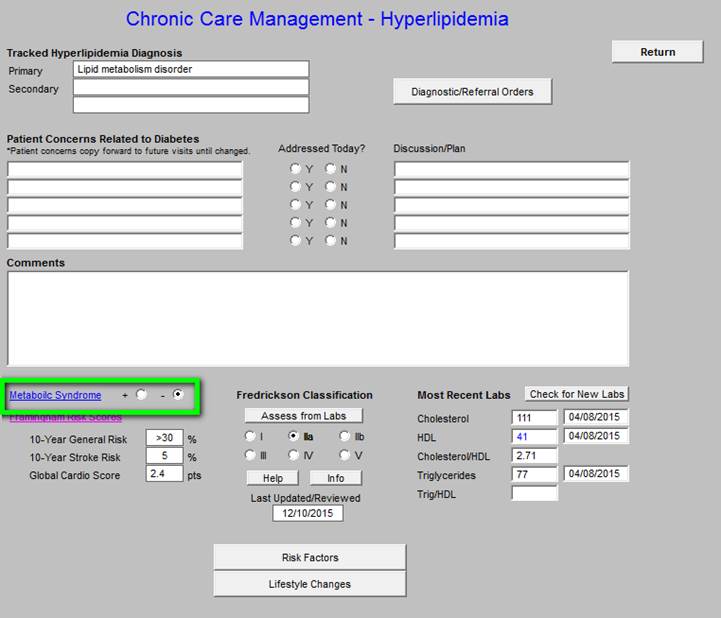
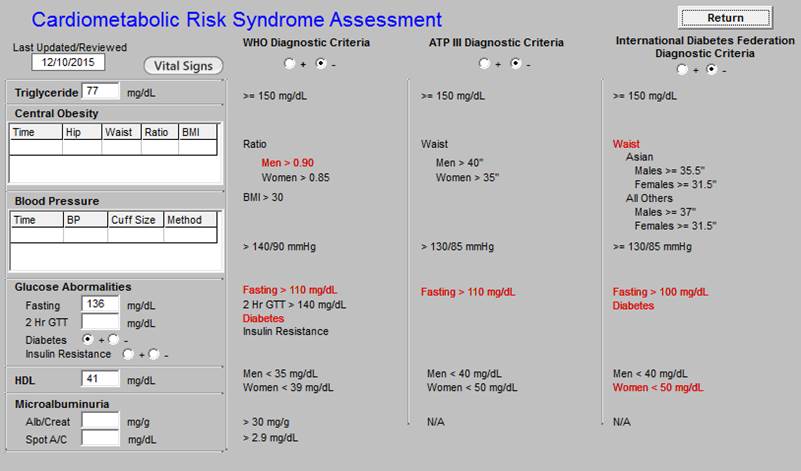
When the above button is clicked for “Metabolic Syndrome,” the below assessment template is deployed.
Following that is the Framingham Risk Score.
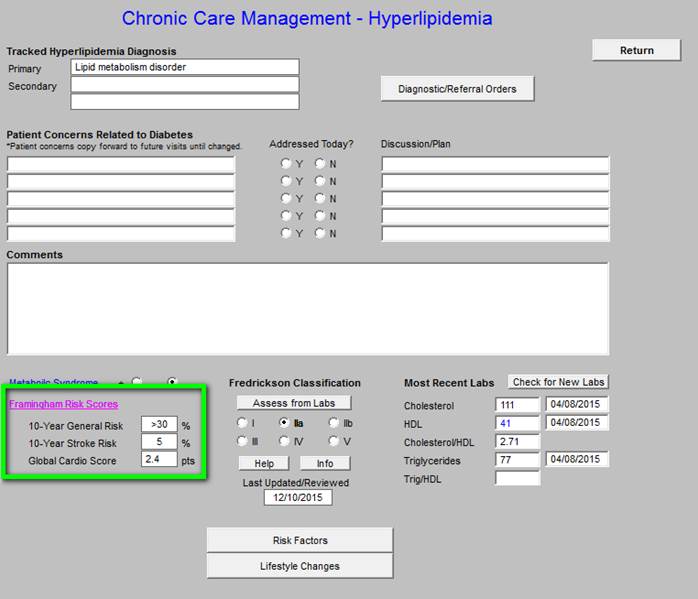
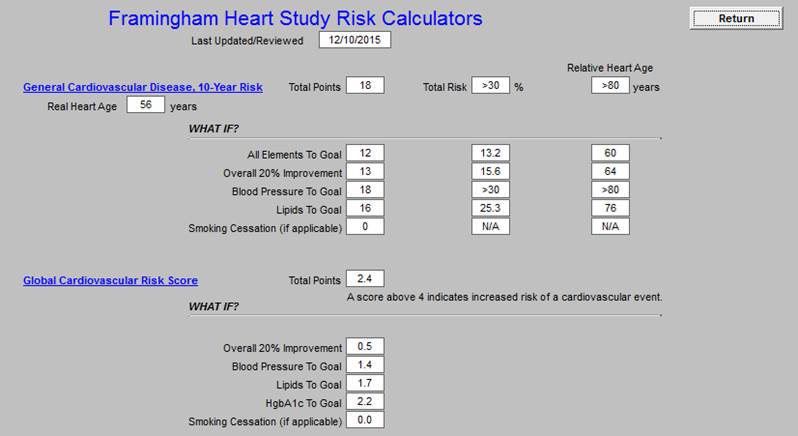
Followed by the Fredrickson Classification of Dyslipidemia.
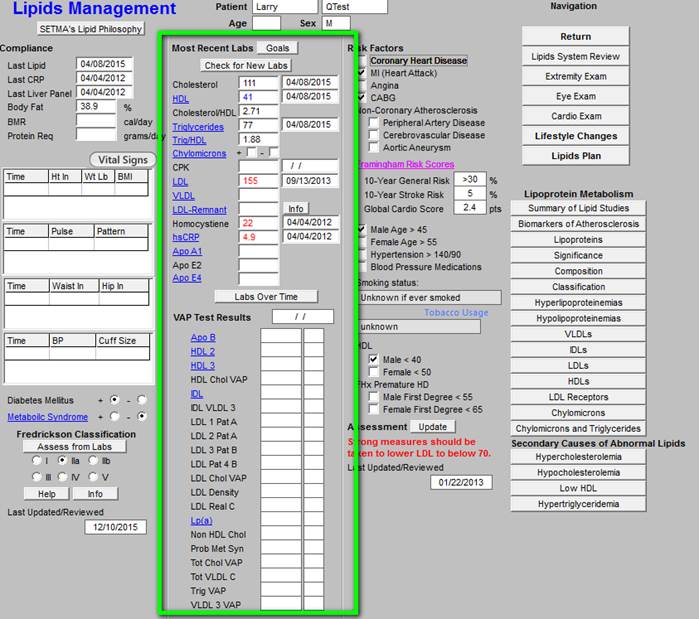
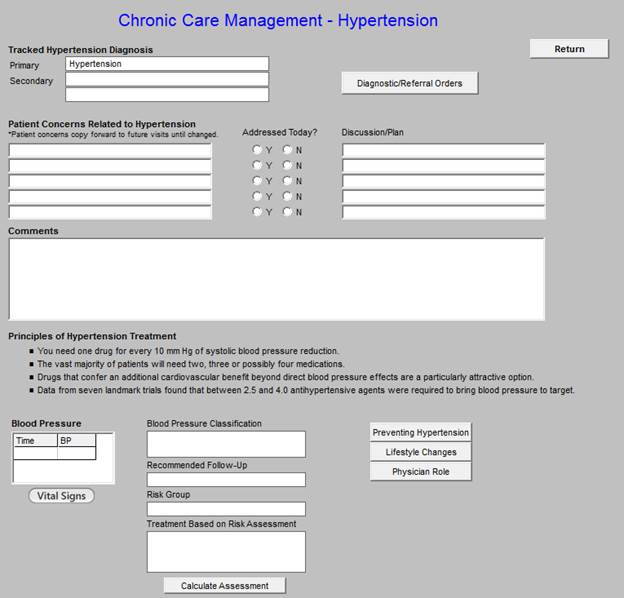
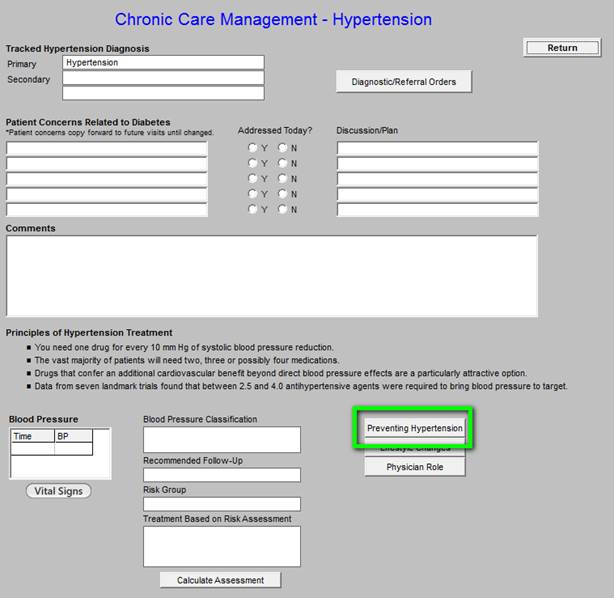
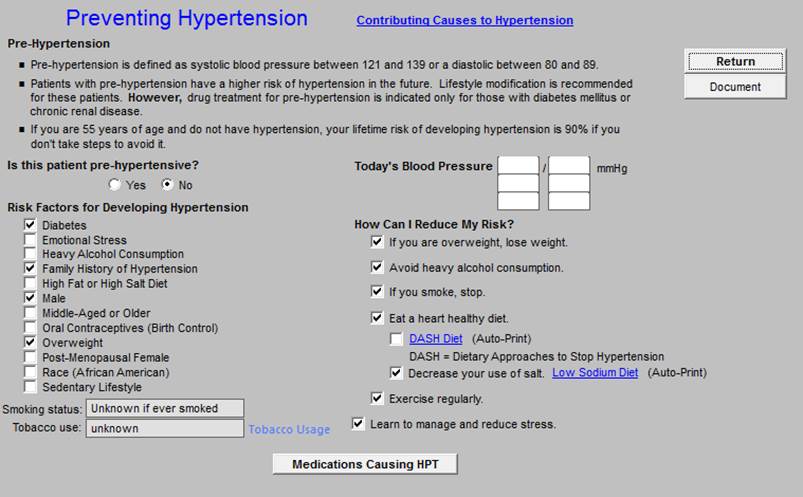
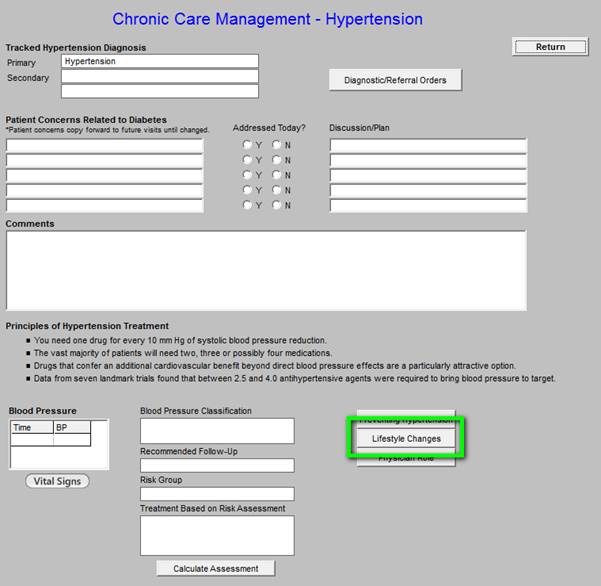
Chronic Care Management -- Hypertension
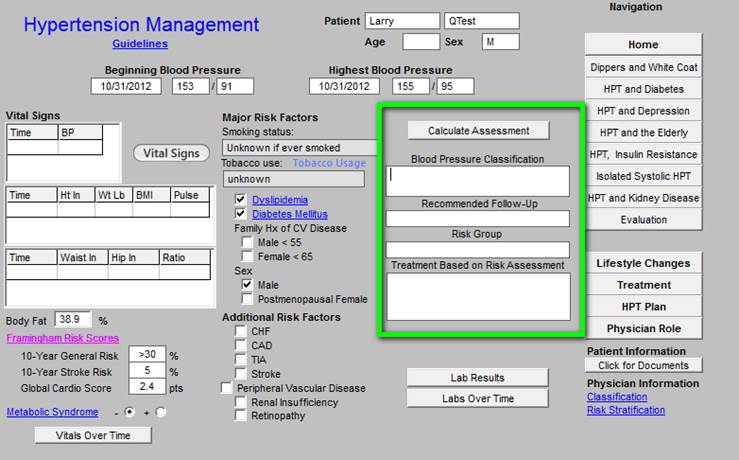

Chronic Care Management - Obesity

|